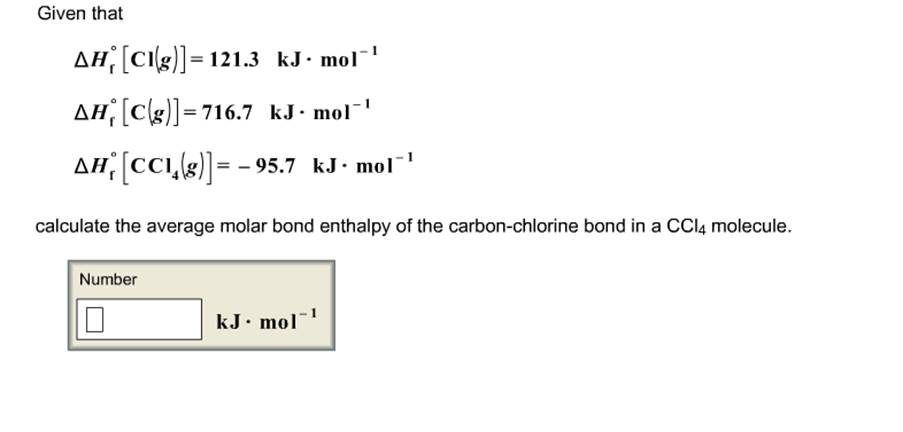
Given that ΔΗ [Cl(g)]=121.3 kJ·mol¹ ΔΗ [C(g)] = 716.7 kJ·mol¹ ΔΗ [CCI(8)] = -95.7 kJ·mol¹ calculate the average molar bond enthalpy of the carbon-chlorine bond in a CCl4 molecule.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
To calculate the average molar bond enthalpy of the carbon-chlorine (C-Cl) bond in a CCl₄ molecule, we can use the information about the enthalpies of formation (ΔH) of the molecules involved in the reaction. The goal is to calculate the energy required to break all C-Cl bonds in a CCl₄ molecule, using the enthalpy values provided.
The given data includes:
- ΔH [Cl(g)] = 121.3 kJ/mol
- ΔH [C(g)] = 716.7 kJ/mol
- ΔH [CCI₄(l)] = -95.7 kJ/mol
Step-by-step approach:
- Write the formation reaction of CCl₄ from its elements:
The formation of CCl₄ from carbon and chlorine in their standard states is: [
C(s) + 2Cl_2(g) \rightarrow CCl_4(l)
] - Calculate the change in enthalpy for the formation of CCl₄:
We can break this reaction into steps and use the provided enthalpy of formation values to calculate the total enthalpy change for the reaction. [
\Delta H_{\text{reaction}} = \left[\text{Enthalpy of products}\right] – \left[\text{Enthalpy of reactants}\right]
] - Use bond enthalpy to calculate energy required to break bonds:
To calculate the average bond enthalpy of the C-Cl bond, we will first determine how much energy is needed to break the bonds in the reactants (Cl₂ molecules) and the energy released when forming the C-Cl bonds in CCl₄.
Calculating the bond enthalpy:
For CCl₄, there are four C-Cl bonds, so the average molar bond enthalpy of a C-Cl bond is obtained by dividing the total bond energy by the number of bonds.
The bond enthalpy of C-Cl can be approximated using Hess’s Law and the steps above. Since we do not have the direct bond enthalpy for C-Cl in the question, we would need to estimate it using bond energies from other references or detailed calculations on the reaction.
Unfortunately, due to the complexity of this reaction and the absence of specific values for bond energies, we cannot calculate the exact bond enthalpy directly without additional information. However, the process typically involves using known bond enthalpies for similar bonds or a more detailed thermodynamic cycle.