Match the major tissue type with its characteristic (A-E). Each letter will only be used once.
Epithelial
Connective
Muscular
Nervous
ÂÂ
A. Contractile
B. Lines structures
C. Information transmission
D. Supportive/Structural
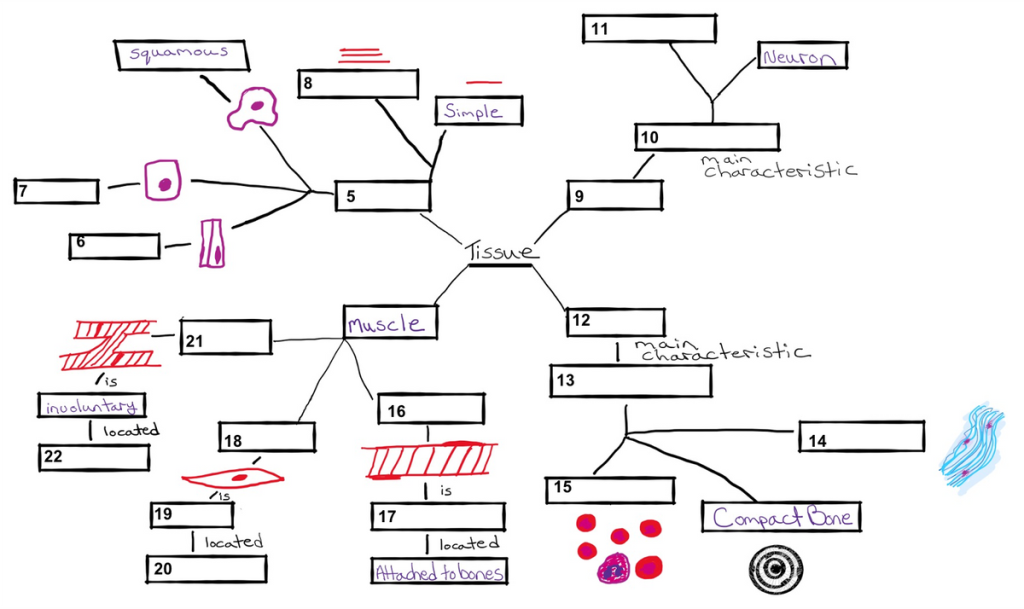
The concept map is on the next page with space to write the answers. Concept
maps are a way to organize your information and everyone does it a little differently.
For this one, follow the flow of the diagram to fill in the correct responses to organize the
tissue information. START with the word TISSUE in the center and go out from there.
There is only 1 correct answer for each box, word bank below (Try without the
word bank too!):
ÂÂ
Word Bank: Epithelial, Connective, Nervous, Voluntary, Involuntary, Blood,
Communication, Skeletal, Smooth, Cardiac, Stratified, Columnar, Neuroglia,
Fibrocartilage, Small Intestine, Cuboidal, Heart, Support.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Let’s break down the matching of the major tissue types with their corresponding characteristics:
- Epithelial Tissue
- B. Lines structures
Epithelial tissue is primarily responsible for forming protective layers around various body structures, such as skin, organs, and blood vessels. It lines cavities and internal organs like the digestive tract, respiratory tract, and other areas. The tissue is involved in both protecting the underlying structures and facilitating absorption, secretion, and exchange. For example, the epithelial cells in the small intestine help with nutrient absorption.
- Connective Tissue
- D. Supportive/Structural
Connective tissue plays a key role in supporting, connecting, and binding other tissues. It includes a diverse range of tissues like bone, blood, cartilage, adipose (fat) tissue, and tendons. Connective tissues typically contain cells embedded in an extracellular matrix, which gives them their supportive and structural properties. Bone tissue, for example, provides support and strength to the body.
- Muscular Tissue
- A. Contractile
Muscular tissue is unique because its primary function is contractility, which means its ability to shorten and generate force. There are three types of muscle tissues: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle is voluntary and is responsible for movement of the skeleton. Smooth muscle is involuntary and controls movements in organs like the digestive tract and blood vessels. Cardiac muscle is involuntary and found in the heart, helping to pump blood.
- Nervous Tissue
- C. Information transmission
Nervous tissue is specialized for communication through electrical impulses. The neurons in this tissue transmit information across the body, enabling various functions like reflexes, movement, perception, and more. Neuroglia (glial cells) provide support and nourishment to neurons, helping them maintain proper function.
Explanation of the Word Bank:
- Epithelial: This tissue is responsible for covering and lining surfaces, and the characteristic “lines structures” refers to this role.
- Connective: The characteristic “supportive/structural” refers to its role in providing support to organs and tissues, as seen in bones and cartilage.
- Muscular: The characteristic “contractile” is a direct reference to the tissue’s ability to contract and facilitate movement or other processes like peristalsis in the intestines.
- Nervous: “Information transmission” is the hallmark of nervous tissue, with neurons transmitting signals throughout the body.
The word bank provided additional information related to the structure and function of these tissues, as seen in the examples given. For instance, the reference to “Voluntary” and “Involuntary” describes types of muscle tissue, while terms like “Heart” or “Small Intestine” point to specific organs composed of these tissues.