Calculate the index of hydrogen deficiency (degrees of unsaturation) for the following molecule with molecular formula C5H1002, and propose a structure for this compound consistent with the following IR, H NMR, and 23C NMR.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The molecular formula C₅H₁₀O₂ indicates a compound with five carbon atoms, ten hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. To determine the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD), we use the formula:
IHD = (2C + 2 – H) / 2
Substituting the given values:
IHD = (2(5) + 2 – 10) / 2 = (10 + 2 – 10) / 2 = 2 / 2 = 1
An IHD of 1 suggests the presence of either one ring or one double bond in the compound.
Given the molecular formula and IHD, a plausible structure is pentanoic acid (valeric acid).
Proposed Structure:
Pentanoic acid consists of a five-carbon chain with a carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end.
Explanation:
- Degree of Unsaturation: The IHD calculation indicates one degree of unsaturation, which corresponds to the carboxyl group (-COOH) in pentanoic acid.
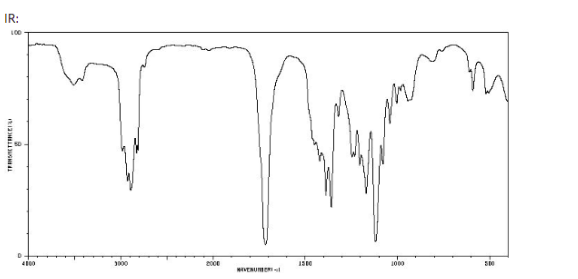
- IR Spectrum: The IR spectrum of pentanoic acid typically shows a strong, broad absorption around 2500–3300 cm⁻¹ due to the O-H stretch of the carboxyl group, and a sharp absorption near 1700 cm⁻¹ for the C=O stretch.
- ¹H NMR Spectrum: In the ¹H NMR spectrum, pentanoic acid exhibits:
- A broad singlet around 11–12 ppm for the carboxylic acid proton.
- Multiplets between 2–3 ppm for the methylene protons adjacent to the carboxyl group.
- Multiplets between 1–2 ppm for the remaining methylene protons in the chain.
- ¹³C NMR Spectrum: The ¹³C NMR spectrum shows:
- A carbonyl carbon signal around 180 ppm.
- Methylene carbon signals between 30–40 ppm.
- Methyl carbon signals around 10–20 ppm.
These spectral features are consistent with the structure of pentanoic acid.
For a visual explanation of the ¹H NMR spectrum of C₅H₁₀O₂, you might find the following video helpful:
video¹H NMR of C₅H₁₀O₂ (pentanoic acid, valeric acid)turn0search6