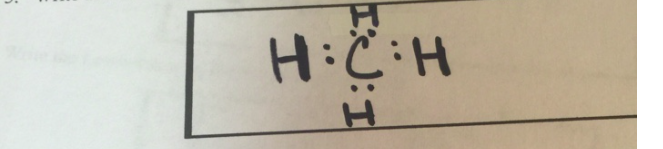
Write The Lewis Structure For Methane, CH4
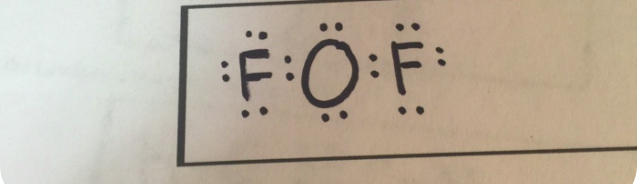
Write The Lewis Structure For Oxygen Difluoride.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
Lewis Structures for Methane (CH₄) and Oxygen Difluoride (OF₂)
Methane (CH₄)
- Step 1: Count the total valence electrons.
- Carbon (C) has 4 valence electrons.
- Hydrogen (H) has 1 valence electron × 4 = 4.
- Total = 4 (C) + 4 (H) = 8 valence electrons.
- Step 2: Arrange the atoms.
- Carbon is the central atom because it is less electronegative than hydrogen.
- Step 3: Distribute electrons.
- Form single bonds between carbon and each hydrogen atom.
- Each single bond uses 2 electrons, for a total of 8 electrons.
- Final Structure:
- Carbon forms 4 single bonds with hydrogen.
- No lone pairs remain on carbon or hydrogen since all valence electrons are used in bonding.
Lewis Structure for CH₄:
H
|
H - C - H
|
HOxygen Difluoride (OF₂)
- Step 1: Count the total valence electrons.
- Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons.
- Fluorine (F) has 7 valence electrons × 2 = 14.
- Total = 6 (O) + 14 (F) = 20 valence electrons.
- Step 2: Arrange the atoms.
- Oxygen is the central atom because it is less electronegative than fluorine.
- Step 3: Distribute electrons.
- Form single bonds between oxygen and each fluorine atom. This uses 4 electrons (2 per bond).
- Distribute the remaining 16 electrons as lone pairs: 6 electrons on each fluorine (to fill their octets) and 4 electrons as lone pairs on oxygen.
- Final Structure:
- Oxygen forms 2 single bonds with fluorine and has 2 lone pairs.
- Each fluorine has 3 lone pairs.
Lewis Structure for OF₂:
F - O - F
: :Explanation
The Lewis structure is a representation of the bonding between atoms and the distribution of valence electrons. For methane (CH₄), carbon forms 4 covalent bonds with hydrogen, satisfying the octet rule for carbon and the duet rule for hydrogen. No lone pairs exist in CH₄ because all valence electrons are used in bonding.
For oxygen difluoride (OF₂), oxygen shares electrons with two fluorine atoms to form single bonds. Fluorine atoms satisfy the octet rule with their lone pairs, while oxygen also satisfies the octet rule with 2 lone pairs of electrons. This structure reflects the molecular geometry of OF₂, which is bent due to lone-pair repulsion on the oxygen atom.