Use Punnett Square for Color Blindness to answer the following questions:
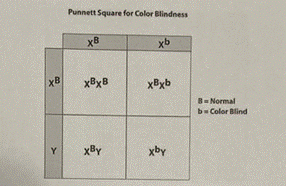
- Which chromosome is the condition of color-blindness inherited upon?
- How many copies of the defective chromosome need be present in order for someone to have colorblindness? Does it differ between males and females? If so, why?
- Do the either of the parents in this example have color blindness? If so, which one (s)?
- Do any of their children have color blindness? Explain what percent of male children will have colorblindness and what percent of female children will have color blindness.
Eye color is actually determined by several genes, but the scenario below is a simplified version:
A dominant allele (P) results in the production of pigment and brown colored eyes. Without this allele, the blue layer at the back of the eye shows through providing blue color. Sam has brown eyes just like his Mom and Dad while his brother, Joe, has blue eyes. Sam’s wife and daughter also have blue eyes.
Answer the following questions using terminology that describes the genotype (not allele letters). You may find it useful to draw a Punnett’s square to determine this pattern of inheritance.
1 What is/are the genotype(s) of Sam’s parents?
2 What is the genotype of Sam’s daughter?
3 Sam’s genotype is
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
It seems I wasn’t able to access the image directly. However, I can help answer the questions based on the general principles of Punnett squares for color blindness, along with the eye color inheritance scenario you provided.
1. Which chromosome is the condition of color-blindness inherited upon?
Color blindness is inherited on the X chromosome. It is a sex-linked recessive trait, meaning the gene responsible for the condition is located on the X chromosome.
2. How many copies of the defective chromosome need to be present in order for someone to have colorblindness? Does it differ between males and females? If so, why?
- Males: Males only have one X chromosome (XY), so they only need one copy of the defective gene on that X chromosome to express color blindness.
- Females: Females have two X chromosomes (XX). They would need two copies of the defective gene (one on each X chromosome) to have color blindness. If they have one defective gene and one normal gene, they will be carriers but won’t express the condition themselves.
3. Do either of the parents in this example have color blindness? If so, which one(s)?
To answer this definitively, I would need to see the image or more information about the parents’ phenotypes. Typically, males with color blindness would show the condition, while females could either show the condition or be carriers (depending on whether they have one or two defective X chromosomes).
4. Do any of their children have color blindness? Explain what percent of male children will have color blindness and what percent of female children will have color blindness.
- If the mother is a carrier (X^C X^c) and the father has normal vision (X^C Y), then:
- Male children: A male child inherits his X chromosome from his mother and his Y chromosome from his father. If the mother passes on the X^c (defective) chromosome, the male child will have color blindness. Thus, 50% of male children will have color blindness.
- Female children: Female children inherit one X chromosome from each parent. If the mother is a carrier and the father has normal vision, the female child will inherit one normal X and one X^c (defective) X chromosome. These female children will be carriers, but will not have color blindness themselves. Thus, none of the female children will have color blindness.
For the Eye Color Questions:
- What is/are the genotype(s) of Sam’s parents?
- Sam has brown eyes, so he must have at least one dominant allele (P). His brother, Joe, has blue eyes, which means both of Sam’s parents must be carriers of the blue-eye gene. Therefore, the genotype of Sam’s parents must be Pp (one brown allele and one blue allele).
- What is the genotype of Sam’s daughter?
- Sam has brown eyes, so his genotype must be Pp. Sam’s wife has blue eyes, so her genotype must be pp. Their daughter could inherit either a P or a p from Sam and a p from her mother. Therefore, her genotype could either be Pp (brown eyes) or pp (blue eyes).
- Sam’s genotype is
Sam has brown eyes, so his genotype must be Pp (heterozygous for the brown-eye allele).
Would you like me to generate a Punnett square for this scenario?