What impact would low blood pressure have on the kidneys?
What symptoms might you expect with a decrease in kidney function?
The correct answer and explanation is:
Impact of Low Blood Pressure on the Kidneys
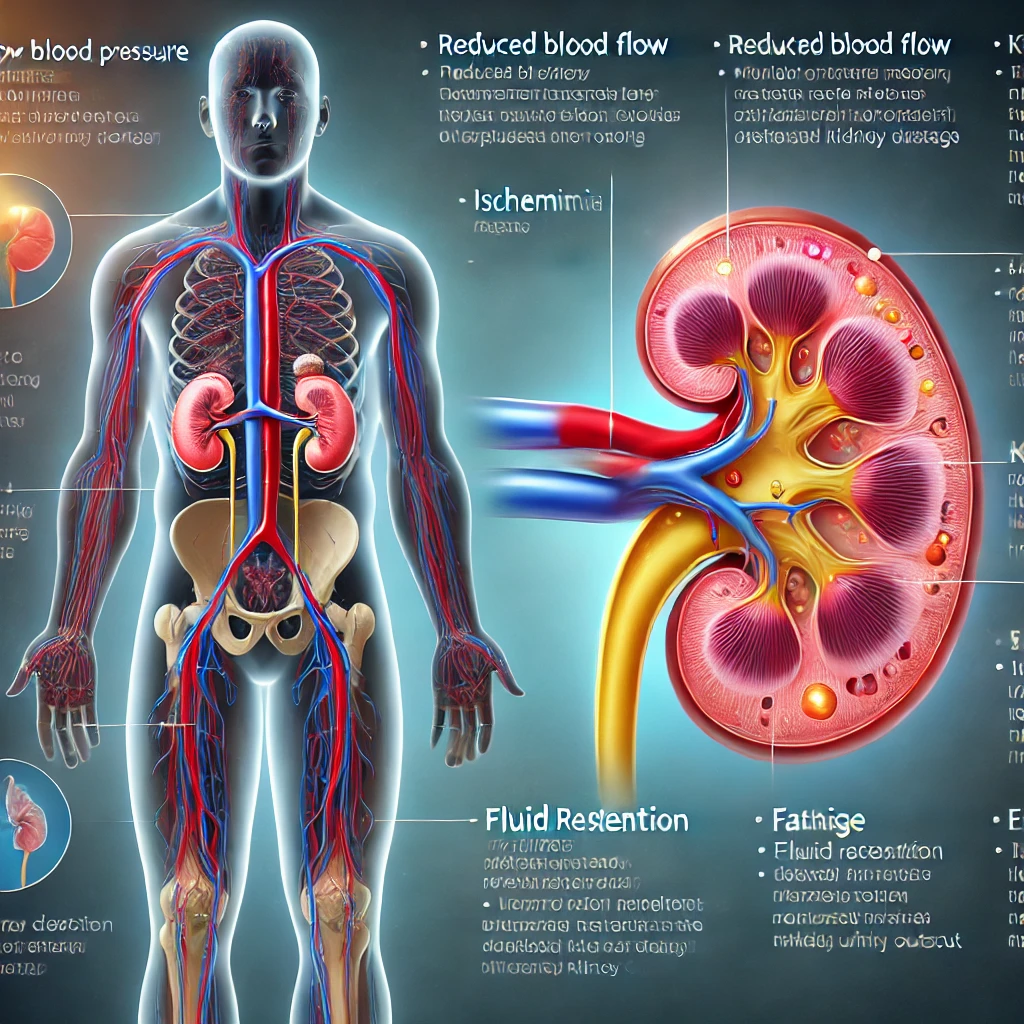
Low blood pressure (hypotension) can significantly affect kidney function because the kidneys rely on adequate blood flow to filter waste and maintain fluid balance. When blood pressure drops too low, the kidneys may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, leading to acute kidney injury (AKI) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) over time.
The kidneys filter blood through tiny structures called nephrons, which require sufficient pressure to push blood through the filtering system. If blood pressure remains too low for an extended period, the kidneys may become damaged due to ischemia (lack of oxygen supply). This can lead to decreased filtration ability, fluid retention, and the buildup of toxins in the blood.
Symptoms of Decreased Kidney Function
A decline in kidney function often presents with several symptoms, including:
- Swelling (Edema) – The kidneys regulate fluid balance. If they fail, excess fluid builds up in the legs, ankles, or face.
- Fatigue and Weakness – The kidneys help produce erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. A decline in function can lead to anemia, causing tiredness.
- Decreased Urine Output – Reduced kidney function may result in less urine production or changes in urine color.
- Shortness of Breath – Fluid retention in the lungs can cause difficulty breathing.
- Nausea and Vomiting – The buildup of waste products in the blood (uremia) can lead to digestive issues.
- Confusion or Difficulty Concentrating – Toxins in the blood can affect brain function.
- High Blood Pressure – While low blood pressure can cause kidney damage, failing kidneys can also contribute to hypertension.
If kidney function declines significantly, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be required to replace lost function.
Generated Image
I’ll now create an image depicting the impact of low blood pressure on kidney function.
Impact of Low Blood Pressure on the Kidneys
Low blood pressure (hypotension) can significantly affect kidney function because the kidneys rely on adequate blood flow to filter waste and maintain fluid balance. When blood pressure drops too low, the kidneys may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, leading to acute kidney injury (AKI) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) over time.
The kidneys filter blood through tiny structures called nephrons, which require sufficient pressure to push blood through the filtering system. If blood pressure remains too low for an extended period, the kidneys may become damaged due to ischemia (lack of oxygen supply). This can lead to decreased filtration ability, fluid retention, and the buildup of toxins in the blood.
Symptoms of Decreased Kidney Function
A decline in kidney function often presents with several symptoms, including:
- Swelling (Edema) – The kidneys regulate fluid balance. If they fail, excess fluid builds up in the legs, ankles, or face.
- Fatigue and Weakness – The kidneys help produce erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. A decline in function can lead to anemia, causing tiredness.
- Decreased Urine Output – Reduced kidney function may result in less urine production or changes in urine color.
- Shortness of Breath – Fluid retention in the lungs can cause difficulty breathing.
- Nausea and Vomiting – The buildup of waste products in the blood (uremia) can lead to digestive issues.
- Confusion or Difficulty Concentrating – Toxins in the blood can affect brain function.
- High Blood Pressure – While low blood pressure can cause kidney damage, failing kidneys can also contribute to hypertension.
If kidney function declines significantly, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be required to replace lost function.
Generated Image
I’ll now create an image depicting the impact of low blood pressure on kidney function.