What is a main difference between active and passive transport?
active transport is spontaneous
active transport requires an energy input (ATP)
passive transport can move molecules against their concentration gradient
active transport uses a protein while passive transport does not
The Correct Answer and Explanation is :
The correct answer is: Active transport requires an energy input (ATP).
Explanation:
Active and passive transport are two primary mechanisms by which molecules move across cell membranes, but they differ significantly in the way they function.
- Energy Requirements:
- Active Transport: This type of transport requires an energy input, usually in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This is because active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient, meaning from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. Since this process is essentially “uphill,” it cannot occur spontaneously without external energy.
- Passive Transport: In contrast, passive transport does not require energy. It relies on the natural tendency of molecules to move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration (down their concentration gradient). This is a spontaneous process, driven by the principles of diffusion and osmosis.
- Movement Direction:
- Active Transport: It can move molecules against their concentration gradient. This means that even if the concentration of a substance is higher outside the cell than inside, active transport can move it into the cell (or vice versa), utilizing energy to do so.
- Passive Transport: Passive transport only allows the movement of molecules in the direction of their concentration gradient. This could involve diffusion (of gases or small molecules), osmosis (for water), or facilitated diffusion (using transport proteins for larger molecules), but it will always move molecules from high to low concentration.
- Use of Proteins:
- Active Transport: In active transport, proteins in the membrane act as “pumps” to actively transport molecules. These proteins change shape when they bind to the molecule and move it across the membrane, using energy from ATP.
- Passive Transport: Some forms of passive transport, such as facilitated diffusion, also use proteins (like channel or carrier proteins) to help molecules cross the membrane, but no energy is required.
In summary, the fundamental difference between active and passive transport lies in the need for energy. Active transport requires energy input (ATP) to move molecules against their gradient, whereas passive transport relies on natural diffusion without energy input.
Let me generate an image that illustrates the differences between active and passive transport.
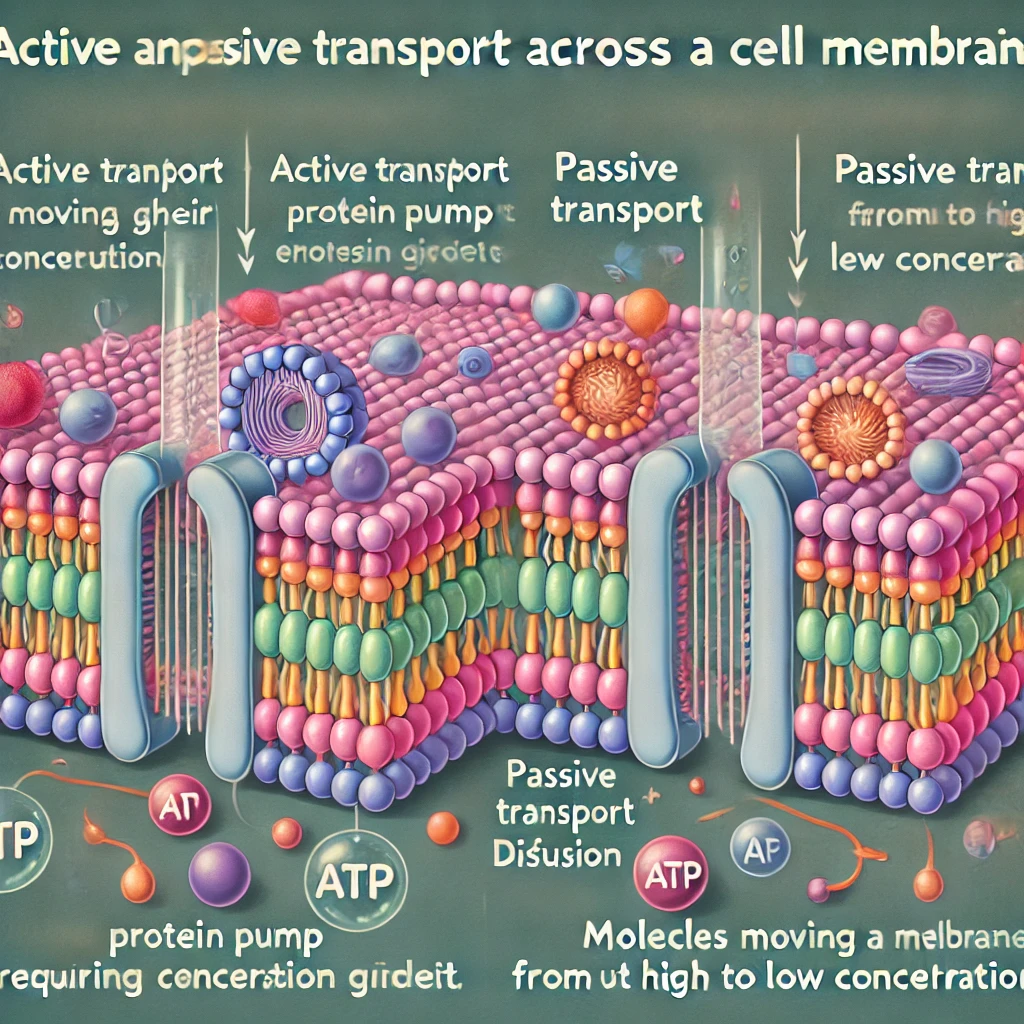
Here is the diagram comparing active and passive transport across a cell membrane. It highlights the key differences, such as the requirement for energy in active transport and the spontaneous nature of passive transport. Let me know if you’d like further clarification!