Use the IS-LM model to answer this question. Suppose there is a simultaneous increase in government spending and reduction in the money supply. Explain what effect this particular policy mix will have on output and the interest rate.
The correct answer and explanation is :
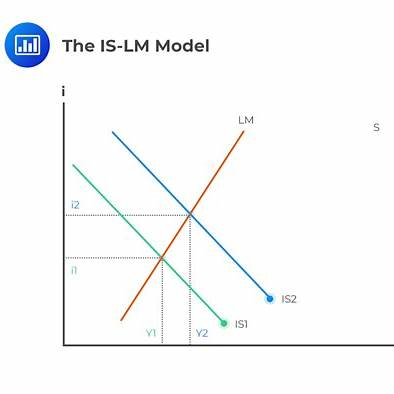
In the IS-LM model, a simultaneous increase in government spending and a reduction in the money supply have opposing effects on output (Y) and the interest rate (i).
Effect on Output (Y):
- Increase in Government Spending: This shifts the IS curve rightward, indicating higher demand for goods and services, leading to an increase in output.
- Reduction in Money Supply: This shifts the LM curve leftward, reflecting reduced liquidity in the economy, which can decrease output.
The net effect on output depends on the magnitudes of these shifts. If the IS curve’s rightward shift (due to increased government spending) is larger than the LM curve’s leftward shift (due to reduced money supply), output will rise. Conversely, if the LM curve’s shift is more pronounced, output may decline.
Effect on Interest Rate (i):
- Increase in Government Spending: The rightward shift of the IS curve leads to higher interest rates as increased demand for funds puts upward pressure on rates.
- Reduction in Money Supply: The leftward shift of the LM curve also leads to higher interest rates due to decreased money availability.
Both policies independently contribute to rising interest rates, making an increase in the interest rate a certain outcome.
Effect on Investment:
Investment is inversely related to the interest rate; higher rates typically reduce investment. While the interest rate is certain to rise, the effect on investment also depends on changes in output:
- If Output Increases: Higher output can boost business prospects, potentially offsetting some negative effects of higher interest rates on investment.
- If Output Decreases or Remains Unchanged: The rise in interest rates is likely to reduce investment.
Therefore, the exact effect on investment is uncertain without knowing the net change in output.
Graphical Representation:
A graph illustrating these shifts would show:
- The IS curve shifting rightward due to increased government spending.
- The LM curve shifting leftward due to reduced money supply.
- The new equilibrium point would be at a higher interest rate, with the change in output depending on the relative shifts of the IS and LM curves.
This analysis highlights the complex interplay between fiscal and monetary policies and their combined impact on economic variables.