what is microbiology and Which microorganism perform photosynthesis by utilizing light?
The correct answer and explanation is :
Microbiology and Photosynthetic Microorganisms
What is Microbiology?
Microbiology is the branch of science that studies microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, algae, and protozoa. These microscopic organisms exist in various environments, playing crucial roles in ecosystems, human health, and industries. Microbiology covers fields such as medical microbiology (study of disease-causing microbes), environmental microbiology (microbes in ecosystems), and industrial microbiology (use of microbes in food and pharmaceuticals).
Microorganisms that Perform Photosynthesis Using Light
Several microorganisms perform photosynthesis by using light energy. The major ones include:
- Cyanobacteria – Also known as blue-green algae, cyanobacteria are the most well-known photosynthetic bacteria. They use chlorophyll-a, similar to plants, and release oxygen during photosynthesis.
- Algae – Various microalgae, including diatoms and green algae, use light to produce energy. They contain chloroplasts with pigments such as chlorophyll-a and -b.
- Purple Sulfur Bacteria – These bacteria use bacteriochlorophyll pigments to absorb light and carry out photosynthesis without producing oxygen. Instead, they utilize hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) rather than water.
- Green Sulfur Bacteria – Similar to purple sulfur bacteria, they perform anoxygenic photosynthesis but use sulfide or other inorganic molecules instead of water.
- Halobacteria (Archaea) – These archaea use bacteriorhodopsin, a light-sensitive protein, to harness light energy, although it is not true photosynthesis as in plants.
Explanation
Photosynthesis is a fundamental biological process where organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, producing organic molecules and, in some cases, oxygen. While plants are well-known for photosynthesis, microorganisms such as cyanobacteria and microalgae are primary contributors to this process, especially in aquatic ecosystems.
Cyanobacteria played a crucial role in Earth’s history by producing oxygen through photosynthesis, leading to the Great Oxygenation Event billions of years ago. These microorganisms continue to contribute significantly to global oxygen levels and carbon fixation.
On the other hand, purple and green sulfur bacteria conduct photosynthesis in anaerobic (oxygen-free) conditions, demonstrating diverse adaptations in microbial photosynthesis.
This microbial capability is crucial for sustaining ecosystems, supporting marine food webs, and even influencing biotechnology applications such as biofuel production.
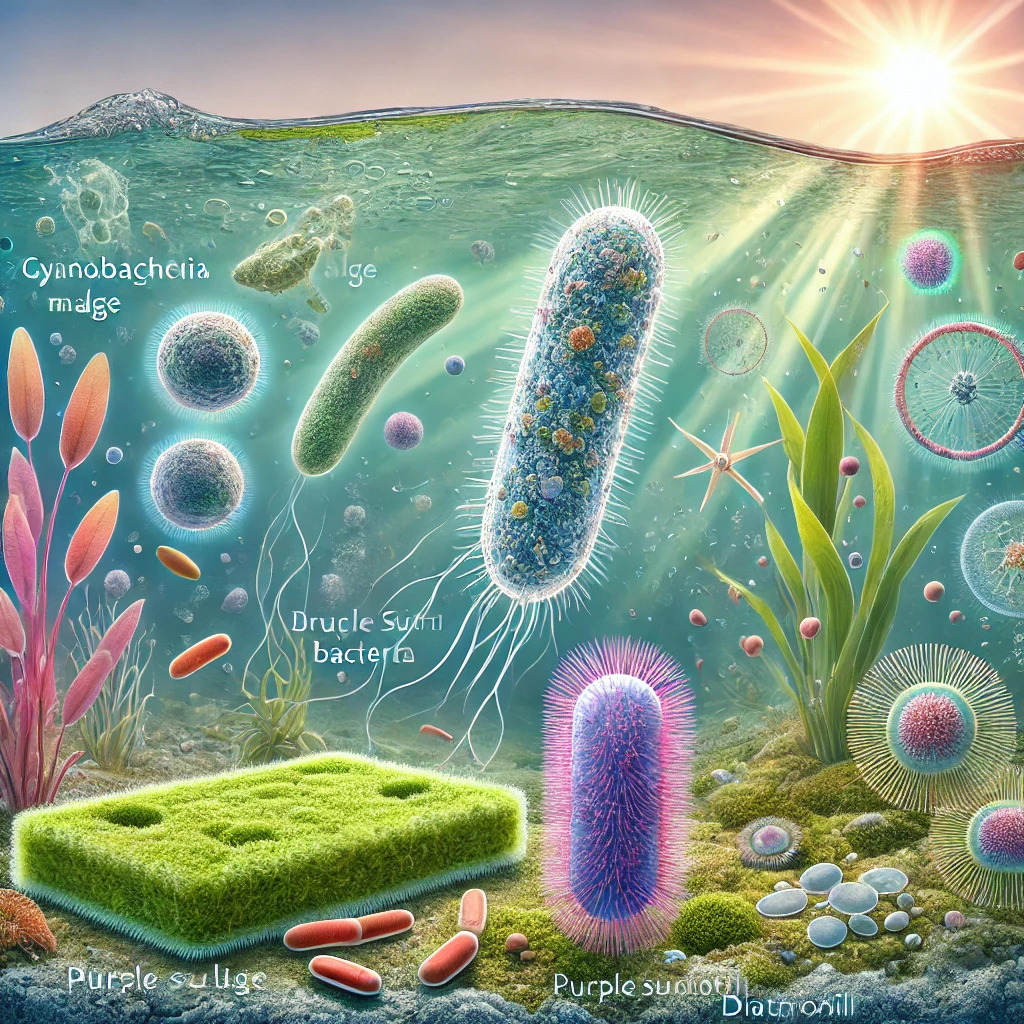
Here is an illustration depicting photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, green algae, purple sulfur bacteria, and diatoms. The image visually represents their cellular structures, pigments, and light absorption process in an aquatic environment.