Label the following structures on the midsagittal section of the brain below. pons corpus callosum cerebellum thalamus cerebral aqueduct
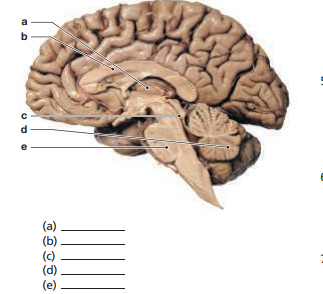
The correct answer and explanation is :
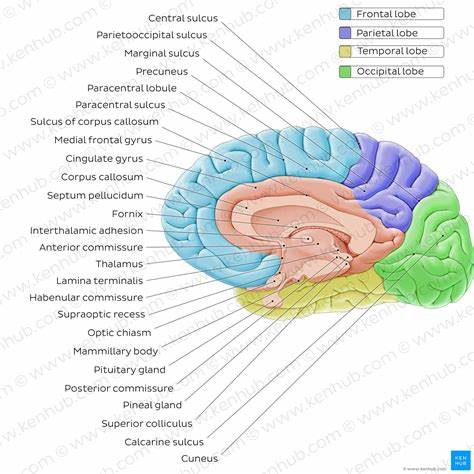
In the provided midsagittal section of the brain, the following structures can be identified and labeled:
- Pons: Located in the brainstem, the pons appears as a prominent bulge above the medulla oblongata. It serves as a bridge connecting the cerebrum with the cerebellum and is crucial for relaying sensory information and regulating vital functions such as respiration.
- Corpus Callosum: This is a thick band of nerve fibers situated superior to the thalamus, arching above the lateral ventricles. It connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres, facilitating interhemispheric communication.
- Cerebellum: Located posterior to the brainstem and inferior to the occipital lobes, the cerebellum has a distinctive, tightly folded appearance. It plays a vital role in motor control, balance, and coordination.
- Thalamus: Situated centrally within the brain, the thalamus is an oval-shaped structure located just above the brainstem. It acts as the brain’s relay station, directing sensory and motor signals to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex.
- Cerebral Aqueduct: This is a narrow channel located within the midbrain, connecting the third and fourth ventricles. It allows the flow of cerebrospinal fluid between these ventricles, playing a role in protecting the brain from trauma and maintaining homeostasis.
Understanding the anatomy of these structures is fundamental in neuroscience and medicine, as they are integral to various neural functions. The pons, for instance, not only relays signals but also plays a role in sleep and arousal. The corpus callosum ensures that both hemispheres of the brain can communicate, which is essential for coordinated function. The cerebellum’s role in fine-tuning motor activity makes it crucial for activities requiring precision. The thalamus’s function as a relay center means it is involved in processing nearly all sensory information. Lastly, the cerebral aqueduct’s role in cerebrospinal fluid circulation is vital for cushioning the brain and removing waste products.
Recognizing these structures and understanding their functions provides insight into the complex orchestration of activities that underlie human thought, emotion, and movement.