What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
The medulla oblongata is responsible for regulating vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It acts as a communication pathway between the brain and the spinal cord and plays a crucial role in autonomic functions.
The correct answer and explanation is :
Function of the Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata is a vital part of the brainstem responsible for regulating essential autonomic functions, including breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It serves as a communication bridge between the brain and spinal cord, ensuring the coordination of involuntary functions necessary for survival.
Detailed Explanation
The medulla oblongata is the lowest part of the brainstem, located just above the spinal cord. It plays a crucial role in autonomic control and contains multiple nuclei that regulate involuntary processes.
1. Control of Vital Functions
- Respiration: The respiratory center in the medulla adjusts breathing rate based on oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
- Heart Rate & Blood Pressure: The cardiovascular center regulates heartbeat and blood pressure by controlling vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels) and vasodilation (widening of blood vessels).
- Swallowing & Digestion: It controls reflexes like swallowing, vomiting, coughing, and sneezing to protect the airway and digestive tract.
2. Nervous System Coordination
- The medulla oblongata contains pathways that connect the brain to the spinal cord, transmitting sensory and motor signals.
- It houses cranial nerve nuclei, which control movements of the tongue, throat, and face.
- The reticular formation, located within the medulla, helps regulate sleep, consciousness, and alertness.
3. Reflex Control
- It manages protective reflexes like sneezing and gagging, ensuring quick responses to stimuli.
- The medulla plays a role in the baroreceptor reflex, which helps maintain stable blood pressure.
Without the medulla oblongata, survival would be impossible, as it controls life-sustaining functions. It acts as the body’s automatic regulator, ensuring homeostasis and adaptation to internal and external changes.
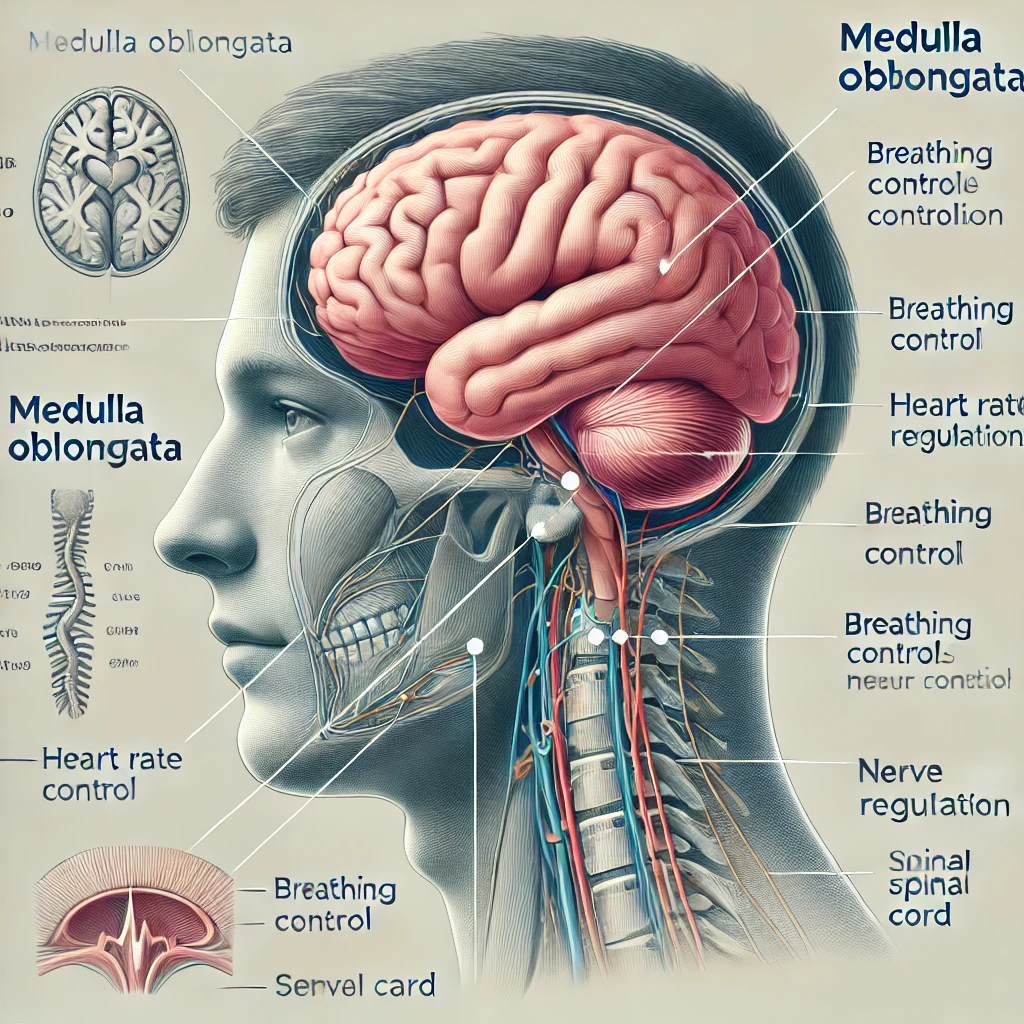
Here is an anatomically detailed illustration of the medulla oblongata, highlighting its location and major functions. Let me know if you need any modifications or further explanations!