A hair dryer is basically a duct in which a few layers of electric resistors are placed. A small fan pulls the air in and forces it to flow over the resistors where it is heated. Air enters a 900-W hair dryer at 100 kPa and 25°C, and leaves at 50°C. The cross-sectional area of the hair dryer at the exit is 60 cm2. Neglecting the power consumed by the fan and the heat losses through the walls of the hair dryer, determine
(a) the volume flow rate of air at the inlet and
(b) the velocity of the air at the exit.
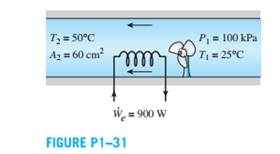
The correct answer and explanation is :
To analyze the performance of a 900-W hair dryer, we can determine:
(a) the volume flow rate of air at the inlet, and
(b) the velocity of air at the exit.
Assumptions:
- Air behaves as an ideal gas.
- Negligible heat losses through the hair dryer walls.
- Negligible power consumption by the fan.
Given Data:
- Power input (𝑊̇): 900
-Inlet pressure (𝑃₁): 100 ka
Inlet temperature (𝑇₁): 25°C = 298.1 K
- Exit temperature (𝑇₂): 50°C = 323.5 K
- Exit cross-sectional area (𝐴₂): 60 cm² = 0.06 m²
- Specific heat capacity of air at constant pressure (𝑐ₚ): approximately 1.005 k/kg·K
- Gas constant for air (𝑅): approximately 0.287 J/kg·K
(a) Volume Flow Rate at the Inlet:
First, we calculate the mass flow rate (𝑚̇) using the energy balance eqution:
𝑊̇ = 𝑚̇ × 𝑐ₚ (𝑇₂ − 𝑇₁)
Rarranging:
𝑚̇ = 𝑊̇ / [�ₚ × (𝑇₂ − 𝑇₁)]
Substituting te given values:
𝑚̇ = 900 W / [1.005 kJ/kg·K × (32.15K − 298.15 K)]
𝑚̇ ≈ 0.0357 kg/s
Next, we determine the specific volume (𝑣₁) at the inlet usingthe ideal gas law:
𝑣₁ = (𝑅 × 𝑇₁) / 𝑃₁
Convrting pressure to kPa:
�₁ = 100 kPa = 100 kPa
𝑣₁ = (0.287 kJkg· × 298.15 K) / 10 kPa
𝑣₁ ≈ 0.855 m³/kg
The volume flow rte (𝑉̇₁) at he nlet is:
𝑉̇₁ = 𝑚̇ × 𝑣₁
𝑉̇ = 0.0357 kg/s × .855 m³/kg
𝑉̇₁ ≈ 0.0305 m³/s
(b) Velocity of Air at the Exit:
First, we calculate the secific volume (𝑣₂ atthe exit:
𝑣₂ = (𝑅 × 𝑇₂) / 𝑃₁
𝑣 = 0.287 kJ/kg·K × 23.15 K) / 100 kPa
𝑣₂ ≈ 0.928 m³/kg
Thevolume flow rte 𝑉̇₂) at the exit is:
𝑉̇₂ = �̇ 𝑣₂
𝑉̇₂ = 00357 kg/s × 0.928 m³/kg
𝑉̇₂ ≈ 0.033 m³/s
Finaly,the exit velocity (𝑉₂) is:
�₂ = 𝑉̇₂ / 𝐴
𝑉₂ = 0.0331 m³/ / 0.006 m²
𝑉₂ ≈ 5.52 m/s
Summary:
(a) The volume flow rte of ar at the inlet is approximately 0.0305 m³/s.
(b) The vlocty of air at the exit is approximately 5.52 m/s.
These calculations provide insight into the thermodynamic behavior of the hair dryer, illustrating how electrical energy input translates into themal energy, affecting air flow rates and velocities.