webcampus.fdu.edu Chordates are a group of organisms that have (#) synapomorphies in common. To start, they have ain) which is a stiff, but flexible rod that extends throughout the length of the organism. Chordates also possess a(n) _nerve cord closely associated with the stiff, but flexible rod. The rod and nerve cord extend into another feature of these organisms, the which humans and frogs have lost. Another trait that adult humans do not have are but we have them during embryonic development. Finally, an endostyle can be found in the pharynx of all chordates. In higher chordates, like humans, the endosytle has become the _gland. Phylum Chordata does not just contain animals with a vertebral column (a.k.a. ). In fact, there are two types of invertebrate chordates that can be found in marine habitats Tunicates are members of subphylum Larval tunicates have all of the synapomorphies of phylum Chordata. However, adult tunicates only possess _Tunicates feed through filter feeding where water and food enter through a(n) and water without food exits through a(n) The other type of invertebrate chordate is commonly called a(n) They are members of subphylum Cephalochordata. 3. There are very few jawless is more Ouay. I c here are less than 100 species of hagfish and
The correct answer and explanation is:
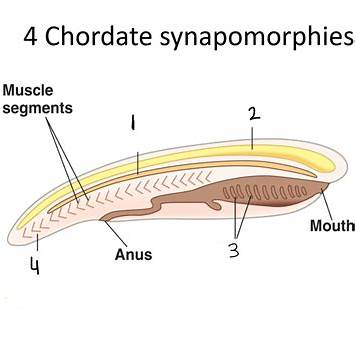
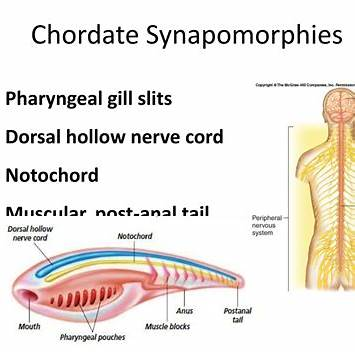
iturn0image0turn0image3turn0image5turn0image8Chordates are a diverse group of organisms characterized by five key synapomorphies:
- Notochord: A stiff, yet flexible rod that extends along the length of the organism, providing structural support.
- Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord: A nerve cord running along the back, closely associated with the notochord.
- Pharyngeal Slits: Openings in the pharynx that, in aquatic species, function in filter feeding or respiration.
- Post-Anal Tail: A tail extending beyond the anus, present during some stage of development.
- Endostyle: A glandular groove in the pharynx involved in filter feeding and iodine metabolism; in higher chordates, it has evolved into the thyroid gland.
The phylum Chordata encompasses both vertebrate and invertebrate species. Notably, there are two groups of invertebrate chordates found in marine habitats:
1. Tunicates (Subphylum Urochordata)
Tunicates, also known as sea squirts, are marine organisms that exhibit all chordate synapomorphies during their larval stage. However, in adulthood, they retain only the endostyle and pharyngeal slits. Tunicates feed through filter feeding, drawing water and food particles into their bodies via an incurrent siphon, and expelling filtered water through an excurrent siphon.
2. Lancelets (Subphylum Cephalochordata)
Commonly referred to as lancelets, these small, fish-like marine animals retain all five chordate characteristics throughout their lives. They are filter feeders, capturing food particles from the water as it passes through their pharyngeal slits.
While the majority of chordates are vertebrates possessing a vertebral column, these invertebrate groups highlight the diversity within the phylum.
Regarding jawless fishes, there are fewer than 100 species of hagfish and lampreys known today. These species are of particular interest due to their primitive features, providing insight into early vertebrate evolution.
Understanding these fundamental traits and the diversity within Chordata offers valuable perspectives on the evolutionary history and adaptability of this phylum.