The change in internal energy of the combustion of solid naphthalene (C10H8) was determined to be equal to -5151 kJ/mol. Calculate its enthalpy of combustion.
What is the change in internal energy of a system if the system evolves 525 J of heat and has 1.25 kJ of work done on it
The correct answer and explanation is :
1. Enthalpy of Combustion of Naphthalene (C₁₀H₈)
The change in internal energy (ΔU) for the combustion of solid naphthalene (C₁₀H₈) is given as -5151 kJ/mol. The relationship between internal energy (ΔU) and enthalpy (ΔH) is given by the following equation:
[
\Delta H = \Delta U + \Delta n \cdot R \cdot T
]
Where:
- ΔH is the enthalpy change
- ΔU is the internal energy change
- Δn is the change in the number of moles of gas (products minus reactants)
- R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K)
- T is the temperature (assumed to be 298 K for standard conditions)
For combustion reactions involving solid naphthalene, the combustion products are gaseous CO₂ and H₂O. The combustion equation for naphthalene is:
[
C_{10}H_8 (s) + 12 O_2 (g) \rightarrow 10 CO_2 (g) + 4 H_2O (g)
]
Now, let’s determine Δn (change in moles of gas):
- On the left side, we have 12 moles of O₂ (gas).
- On the right side, we have 10 moles of CO₂ (gas) and 4 moles of H₂O (gas).
Thus, Δn = (10 + 4) – 12 = 2.
Now, applying the equation to calculate ΔH:
[
\Delta H = \Delta U + \Delta n \cdot R \cdot T = -5151 \, \text{kJ/mol} + (2) \cdot (8.314 \, \text{J/mol·K}) \cdot (298 \, \text{K})
]
First, convert the gas constant to kJ for consistency with the units of ΔU:
[
\Delta H = -5151 \, \text{kJ/mol} + (2 \cdot 8.314 \cdot 298) / 1000
]
[
\Delta H = -5151 \, \text{kJ/mol} + 4.95 \, \text{kJ/mol}
]
[
\Delta H = -5146.05 \, \text{kJ/mol}
]
Thus, the enthalpy of combustion of solid naphthalene is approximately -5146.05 kJ/mol.
2. Change in Internal Energy of a System
The change in internal energy of a system can be determined using the following equation:
[
\Delta U = Q – W
]
Where:
- ΔU is the change in internal energy
- Q is the heat evolved (or absorbed) by the system
- W is the work done by or on the system
Given:
- Q = 525 J (heat evolved by the system)
- W = 1.25 kJ = 1250 J (work done on the system)
Now, substitute these values into the equation:
[
\Delta U = 525 \, \text{J} – 1250 \, \text{J}
]
[
\Delta U = -725 \, \text{J}
]
Thus, the change in internal energy of the system is -725 J.
Explanation
- Enthalpy of Combustion of Naphthalene:
- The combustion reaction of solid naphthalene involves the conversion of a solid to gaseous products (CO₂ and H₂O), leading to a release of heat. The internal energy change (ΔU) is given as -5151 kJ/mol, which reflects the heat released during combustion.
- The difference between enthalpy (ΔH) and internal energy (ΔU) is accounted for by the change in the number of moles of gas produced in the reaction, which is why we apply the equation ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT.
- Change in Internal Energy of a System:
- In the second part, the system undergoes a process where heat is released (525 J) and work is done on it (1.25 kJ). Since heat is released (positive Q), and work is done on the system (positive W), the internal energy decreases because the work done on the system is greater than the heat released. Therefore, the internal energy change is negative, -725 J.
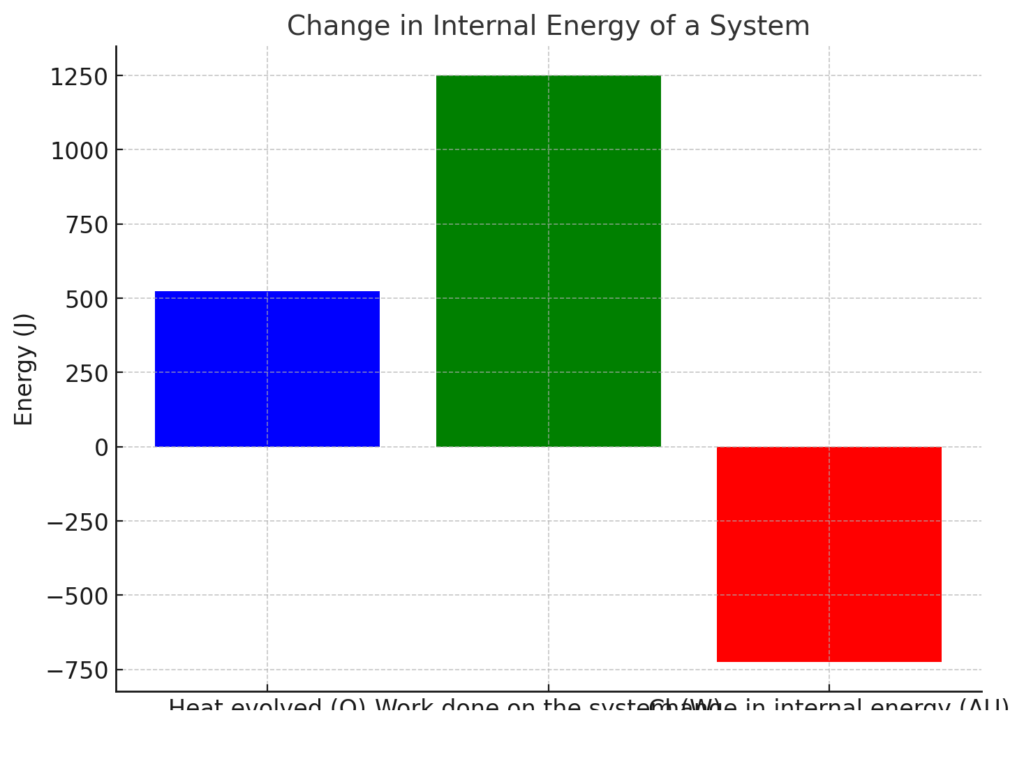
Here is a visual representation of the change in internal energy of the system:
- The first bar shows the heat evolved (525 J).
- The second bar represents the work done on the system (1.25 kJ or 1250 J).
- The third bar shows the total change in internal energy (ΔU), which is -725 J.