The taste of sour milk is lactic acid. What is the molecular formula for lactic acid if the percent composition is 40.00% of C, 6.71% of H, 53.29% of O and the approximate molar mass is 90 g/mol
a. CH2O
b. CHO2
c. C3H6O3
d. CHO
e. C6HO8
The correct answer and explanation is :
Answer: c. C₃H₆O₃
Explanation:
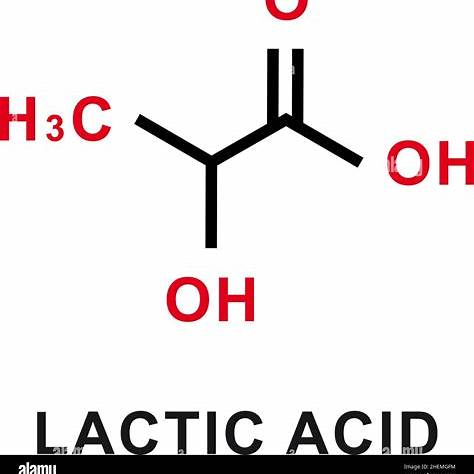
Lactic acid, responsible for the sour taste in fermented dairy products like sour milk, has the molecular formula C₃H₆O₃. To determine this, we can follow these steps:
- Calculate the Empirical Formula: Given the percent composition:
- Carbon (C): 40.00%
- Hydrogen (H): 6.71%
- Oxygen (O): 53.29% Assuming a 100 g sample, the masses of each element are:
- Carbon: 40.00 g
- Hydrogen: 6.71 g
- Oxygen: 53.29 g Convert these masses to moles:
- Carbon: 40.00 g / 12.01 g/mol ≈ 3.33 mol
- Hydrogen: 6.71 g / 1.008 g/mol ≈ 6.66 mol
- Oxygen: 53.29 g / 16.00 g/mol ≈ 3.33 mol Determine the simplest whole-number ratio by dividing each by the smallest number of moles (3.33 mol):
- Carbon: 3.33 mol / 3.33 mol = 1
- Hydrogen: 6.66 mol / 3.33 mol ≈ 2
- Oxygen: 3.33 mol / 3.33 mol = 1 This gives the empirical formula CH₂O.
- Determine the Molecular Formula: The empirical formula mass is:
- C: 12.01 g/mol
- H₂: 2.016 g/mol
- O: 16.00 g/mol Total = 12.01 + 2.016 + 16.00 = 30.026 g/mol Given the approximate molar mass of lactic acid is 90 g/mol, calculate the ratio: 90 g/mol / 30.026 g/mol ≈ 3 Multiply the empirical formula by this ratio:
- Carbon: C₃
- Hydrogen: H₆
- Oxygen: O₃ Thus, the molecular formula is C₃H₆O₃.
Structural Representation:
The structural formula of lactic acid is:
HO-CH₂-CH(OH)-COOHThis structure consists of a three-carbon chain with a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached, characteristic of lactic acid.