A red blood cell will undergo hemolysis in
A) water.
B) 0.9% NaCl.
C) 5% glucose.
D) 5% NaCl.
E) 10% glucose
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct answer is A) water.
Explanation:
Hemolysis is the rupture or destruction of red blood cells (RBCs), which results in the release of hemoglobin and other intracellular contents into the surrounding fluid. This process is closely related to the osmotic pressure exerted by the surrounding solution.
The key factor in hemolysis is osmolarity or tonicity. The tonicity of a solution refers to the relative concentration of solutes in the solution compared to the inside of the red blood cell. A solution can be hypotonic, isotonic, or hypertonic to the cells:
- Hypotonic solutions: These have a lower concentration of solutes compared to the inside of the cell. Water is a classic hypotonic solution since it contains no solutes. When a red blood cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water enters the cell by osmosis, causing it to swell and potentially burst (hemolysis).
- Isotonic solutions: These solutions have the same concentration of solutes as the inside of the red blood cell. A 0.9% NaCl solution (saline) is an example of an isotonic solution. In this case, water moves in and out of the cell at the same rate, and no hemolysis occurs.
- Hypertonic solutions: These have a higher concentration of solutes than the inside of the red blood cell. In hypertonic solutions, water moves out of the red blood cell, causing it to shrink (crenation), not undergo hemolysis. Examples include a 5% NaCl or 10% glucose solution.
In summary, water is a hypotonic solution and will cause water to enter the red blood cells, leading to their rupture and hemolysis. On the other hand, 0.9% NaCl and 5% glucose are isotonic solutions, and 5% NaCl and 10% glucose are hypertonic solutions, all of which would not cause hemolysis under normal circumstances.
Image:
Here is an illustration of how red blood cells behave in different solutions:
- In water (hypotonic solution), the cell swells and bursts.
- In 0.9% NaCl (isotonic solution), the cell remains the same size.
- In 5% NaCl or 10% glucose (hypertonic solutions), the cell shrinks.
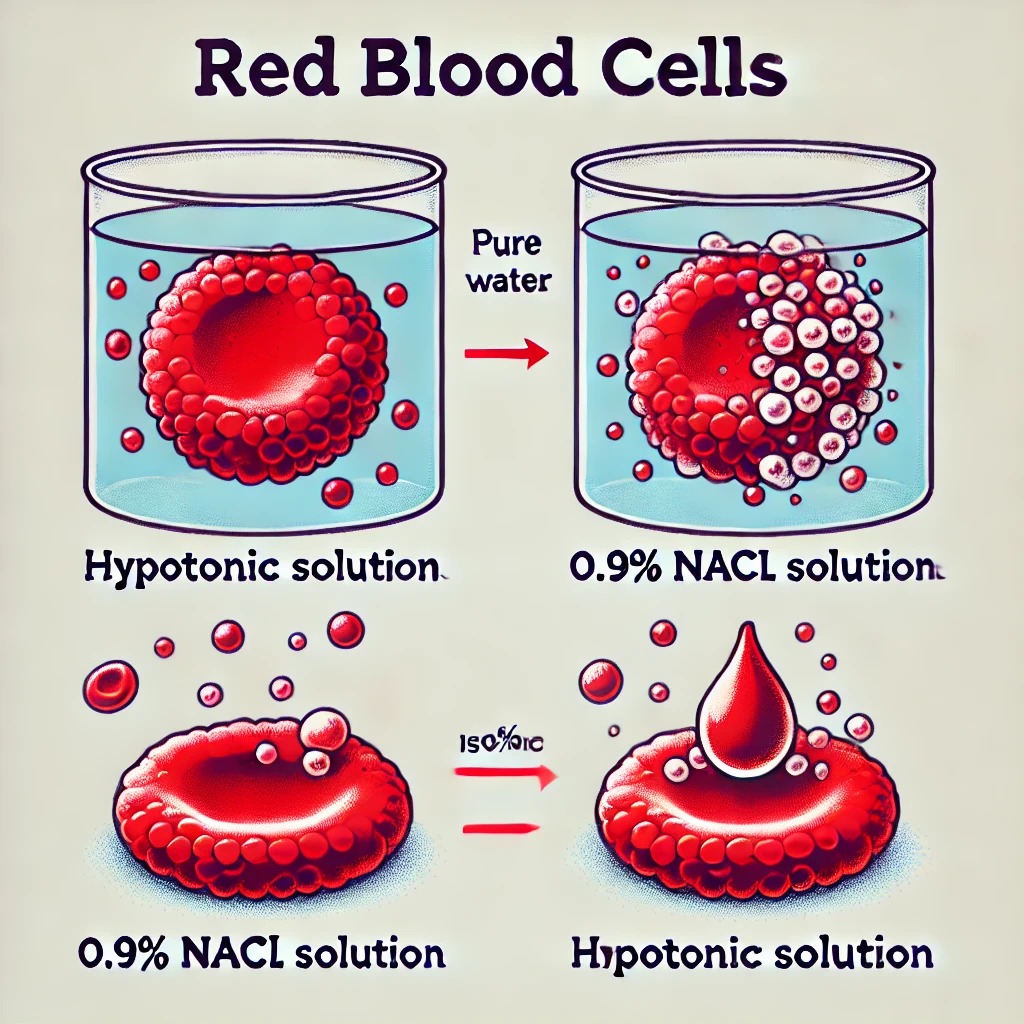
Here is an illustration showing the behavior of red blood cells in different solutions. It demonstrates how the cell reacts to water (hypotonic), 0.9% NaCl (isotonic), and 5% NaCl (hypertonic). In water, the red blood cell swells and bursts, while in isotonic and hypertonic solutions, the cell either stays the same size or shrinks, respectively.