Parathyroid hormone does all of the following, except that it doesn’t
stimulate osteoclast activity
enhance the reabsorption of calcium at the kidneys
build up bone
stimulate the formation and secretion of calcitriol at the kidneys
inhibit osteoblast activity
The correct answer and explanation is :
Correct Answer: “build up bone”
Explanation:
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is a key regulator of calcium homeostasis in the body, primarily increasing blood calcium levels. It is secreted by the parathyroid glands in response to low blood calcium levels. Let’s analyze each of the provided options:
- Stimulate Osteoclast Activity ✅
- PTH stimulates osteoclasts indirectly by signaling osteoblasts to produce RANKL (Receptor Activator of Nuclear factor Kappa-B Ligand), which promotes the differentiation and activity of osteoclasts. Osteoclasts break down bone tissue, releasing calcium into the bloodstream.
- Enhance Reabsorption of Calcium at the Kidneys ✅
- PTH increases calcium reabsorption in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium loss in urine.
- Build Up Bone ❌ (Correct Answer – PTH does not do this!)
- While PTH interacts with osteoblasts, its overall effect is not to build bone, but rather to increase blood calcium by breaking down bone. In contrast, calcitonin (produced by the thyroid gland) promotes bone-building by stimulating osteoblast activity.
- Stimulate the Formation and Secretion of Calcitriol at the Kidneys ✅
- PTH stimulates the kidneys to produce calcitriol (active vitamin D3), which increases calcium absorption from the intestines.
- Inhibit Osteoblast Activity ✅
- While PTH initially stimulates osteoblasts, prolonged exposure inhibits osteoblast function, reducing new bone formation.
Thus, PTH does not build bone, making “build up bone” the correct answer.
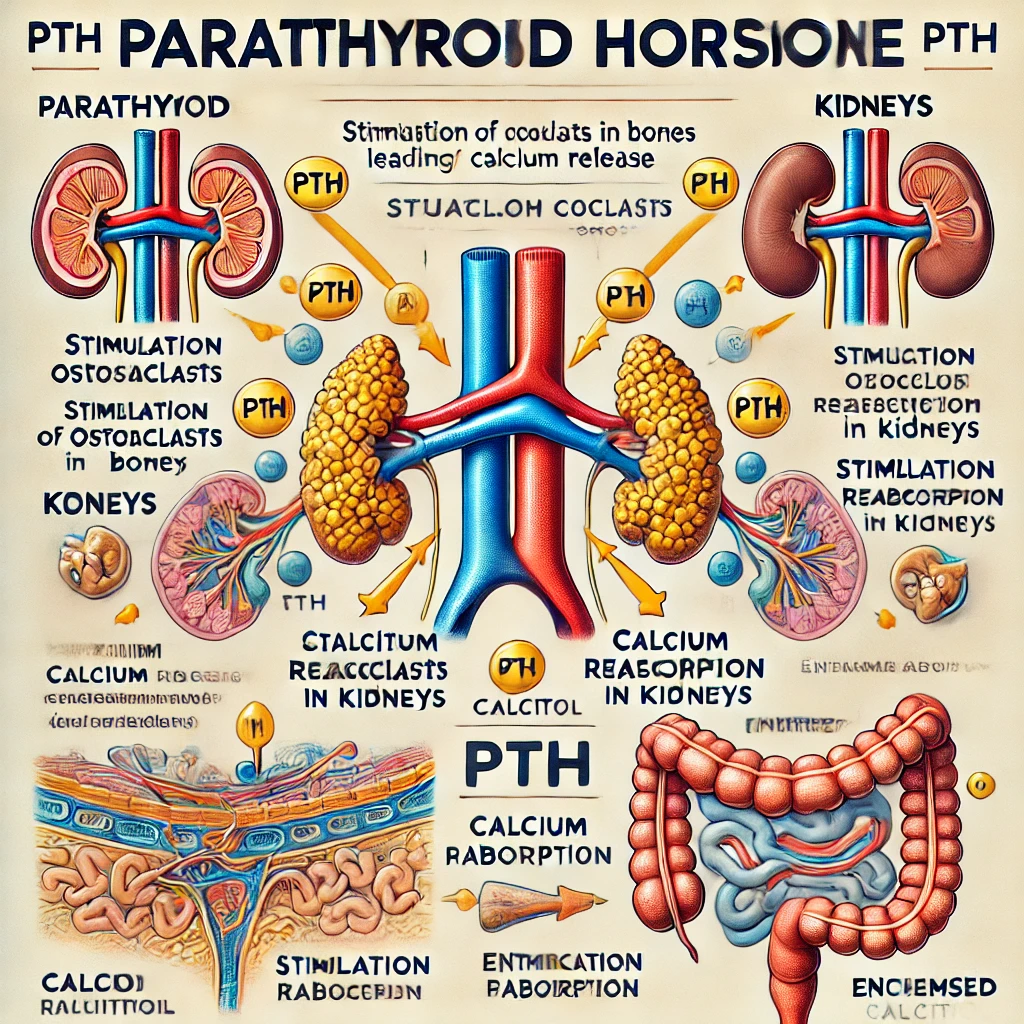
Here is an educational diagram illustrating the functions of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH). It highlights the key effects of PTH on bones, kidneys, and intestines, helping to understand its role in calcium homeostasis.