Explain the concept of weathering and erosion in geography, and discuss their role in shaping Earth’s surface features.
The correct answer and explanation is :
Weathering and Erosion in Geography
Weathering and erosion are natural processes that shape the Earth’s surface over time. Though they are often mentioned together, they are distinct processes.
- Weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals into smaller particles by physical, chemical, or biological processes.
- Erosion is the movement of these weathered particles by natural forces such as wind, water, ice, and gravity.
Types of Weathering:
- Physical Weathering: Also known as mechanical weathering, this occurs when rocks break down without chemical changes. Examples include freeze-thaw action, thermal expansion, and exfoliation.
- Chemical Weathering: Involves chemical reactions that dissolve or alter minerals in rocks. Common processes include oxidation (rusting), hydrolysis, and carbonation.
- Biological Weathering: Caused by living organisms such as plant roots breaking rocks apart or microorganisms producing acids that dissolve minerals.
Erosion and Its Agents:
Once rocks are broken down, erosion transports the particles. The main agents of erosion include:
- Water: Rivers, waves, and rainfall wash away sediments, forming valleys, canyons, and coastal landforms.
- Wind: Wind erosion creates sand dunes and shapes desert landscapes.
- Ice: Glaciers erode landscapes by plucking and abrasion, carving out U-shaped valleys.
- Gravity: Landslides and rockfalls move materials downhill.
Role in Shaping Earth’s Surface
Weathering and erosion are responsible for forming and modifying landscapes such as mountains, valleys, cliffs, beaches, and caves. For example, the Grand Canyon was carved by the Colorado River through continuous erosion over millions of years. Similarly, coastal erosion forms sea arches, stacks, and cliffs.
These processes are essential in the rock cycle and contribute to soil formation, shaping Earth’s dynamic surface.
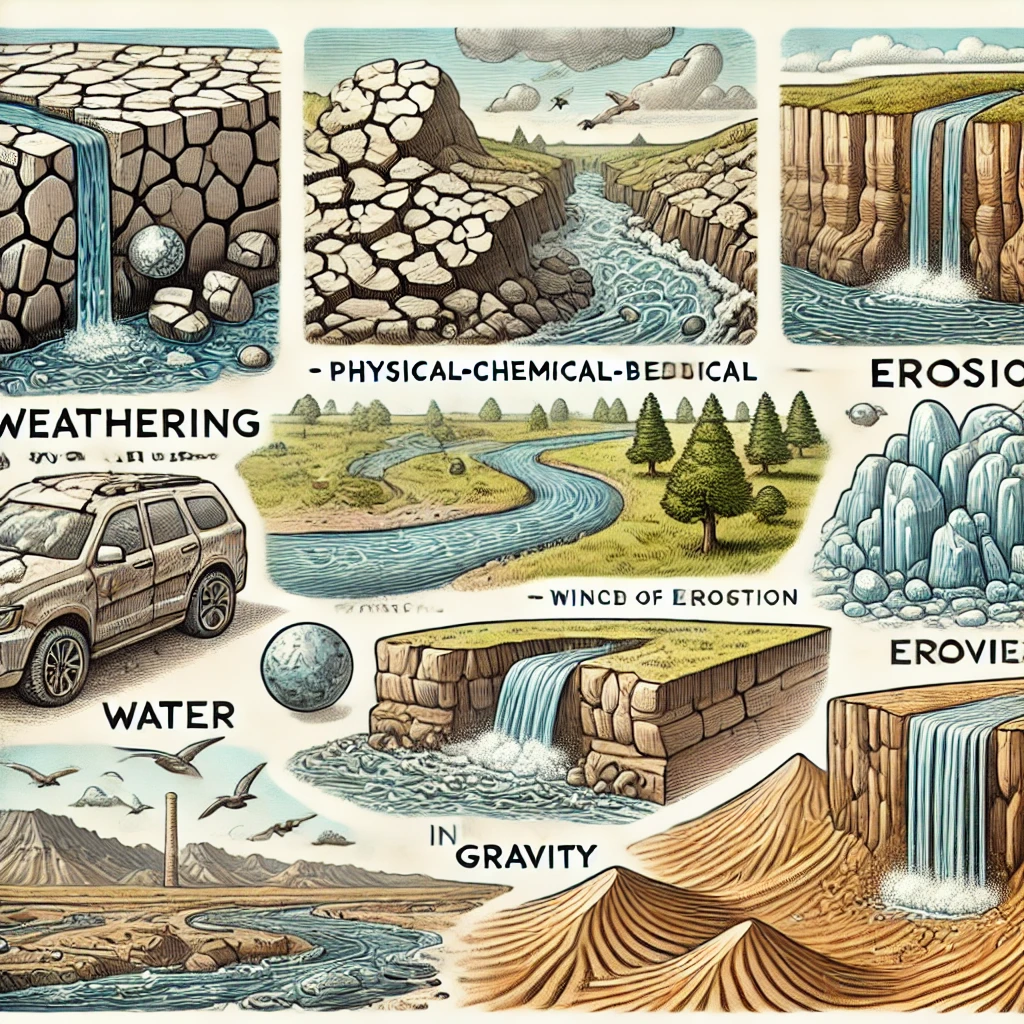
Here is an illustration depicting weathering and erosion processes, including physical, chemical, and biological weathering, as well as erosion by water, wind, ice, and gravity.