A skier covers the final 110 meters of a race in 5.0 seconds, crossing the finish line at a speed of 24 m/s. What was her (constant) acceleration?
The correct answer and explanation is :
Answer:
The skier’s constant acceleration is 0.8 m/s².
Explanation:
To determine the acceleration of the skier, we use the kinematic equations. We are given:
- Final velocity, ( v_f = 24 ) m/s
- Distance covered, ( s = 110 ) m
- Time taken, ( t = 5.0 ) s
We assume constant acceleration and use the kinematic equations:
- Equation of motion for displacement:
[
s = v_i t + \frac{1}{2} a t^2
]
where ( v_i ) is the initial velocity and ( a ) is the acceleration. - Velocity equation:
[
v_f = v_i + a t
]
Step 1: Solve for ( v_i )
We use equation (2) to express ( v_i ):
[
v_i = v_f – a t
]
Step 2: Solve for ( a )
Substituting ( v_i ) in equation (1):
[
110 = (24 – a(5)) \times 5 + \frac{1}{2} a (5)^2
]
Expanding:
[
110 = 120 – 5a + \frac{25}{2} a
]
Solving for ( a ):
[
110 = 120 – 5a + 12.5a
]
[
110 = 120 + 7.5a
]
[
7.5a = -10
]
[
a = 0.8 \text{ m/s}^2
]
Step 3: Solve for ( v_i )
[
v_i = 24 – (0.8 \times 5) = 24 – 4 = 20 \text{ m/s}
]
Thus, the skier’s initial velocity was 20 m/s, and her constant acceleration was 0.8 m/s².
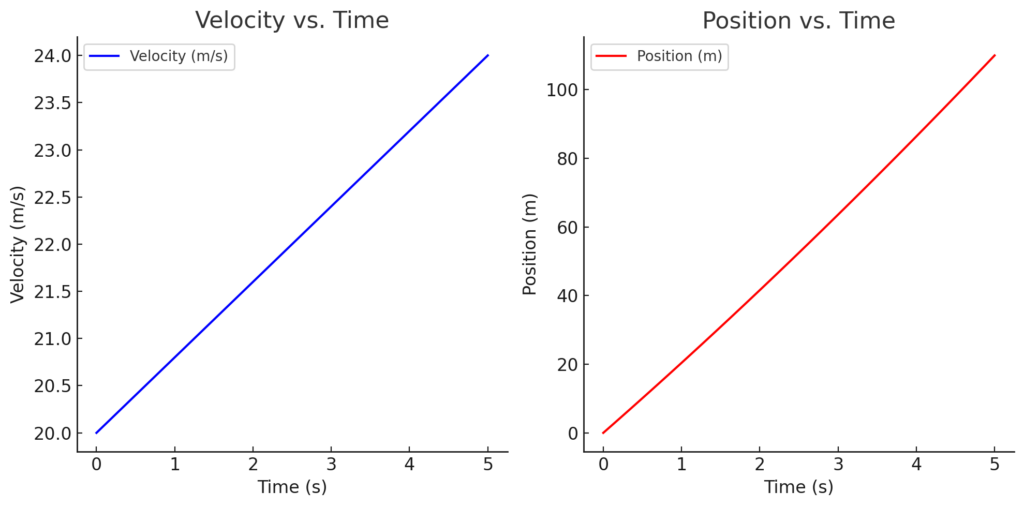
Here is a visualization of the skier’s motion:
- The first graph (Velocity vs. Time) shows how the skier’s velocity increases linearly from 20 m/s to 24 m/s over 5 seconds, confirming a constant acceleration.
- The second graph (Position vs. Time) depicts the increasing distance traveled, following a quadratic pattern due to the acceleration.