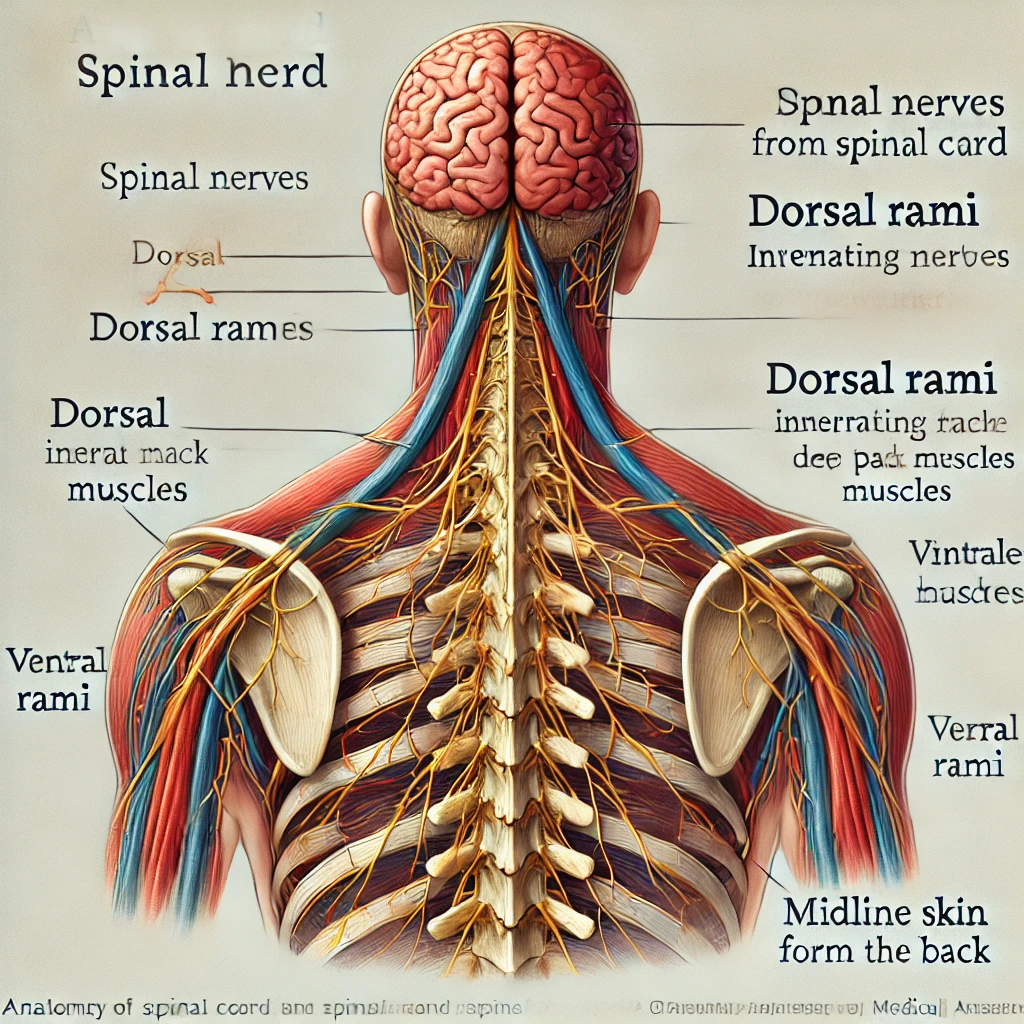
The dorsal rami
Check All That Apply
form nerve plexuses.
form nerve plexuses.
innervate deep muscles of the dorsal trunk.
innervate deep muscles of the dorsal trunk.
innervate intercostal muscles.
innervate intercostal muscles.
innervate skin near the midline of the back.
The correct answer and explanation is :
Correct Answers:
✅ Innervate deep muscles of the dorsal trunk
✅ Innervate skin near the midline of the back
Explanation:
The dorsal rami (singular: ramus) are branches of spinal nerves that emerge from the dorsal root of the spinal cord. They play a crucial role in innervating the back muscles and skin.
1. Innervate Deep Muscles of the Dorsal Trunk ✅
- The dorsal rami supply the deep muscles of the back, also known as intrinsic back muscles. These include:
- Erector spinae muscles (iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis) – responsible for maintaining posture and extending the spine.
- Transversospinalis muscles (semispinalis, multifidus, rotatores) – important for spinal stability and small rotational movements.
- Splenius muscles (splenius capitis, splenius cervicis) – involved in head and neck movements.
2. Innervate Skin Near the Midline of the Back ✅
- The dorsal rami provide sensory innervation to the skin of the back along the midline, extending from the neck to the sacrum.
- This is essential for sensation, touch, pain, and temperature perception in the back region.
Incorrect Options:
❌ Form Nerve Plexuses
- Unlike the ventral rami, which form plexuses (such as the brachial and lumbar plexuses), the dorsal rami do not form nerve plexuses.
- Instead, they remain separate and individually supply specific muscles and skin of the back.
❌ Innervate Intercostal Muscles
- The intercostal muscles (muscles between the ribs) are innervated by the ventral rami of thoracic spinal nerves, not the dorsal rami.
- The ventral rami give rise to intercostal nerves, which control respiration by activating intercostal muscles.
Summary:
- The dorsal rami do not form plexuses and do not innervate intercostal muscles.
- They innervate the deep muscles of the back and provide sensory input to the skin near the midline of the back.