Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in this diagram.
First use the labels of Group 1 to identify the atoms and charges.
Then use the labels of Group 2 to identify the bonds.
Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all.
The correct answer and explanation is :
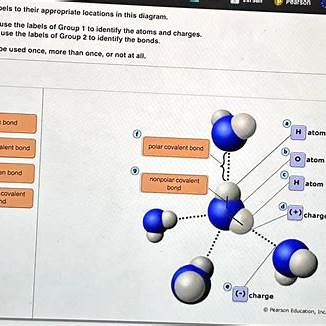
In the given diagram, we are tasked with labeling atoms, their charges, and the types of bonds between them. The labels provided are divided into two groups:
Group 1: Atoms and Charges
- H atom
- O atom
- (+) charge
- (-) charge
Group 2: Bonds
- polar covalent bond
- nonpolar covalent bond
- hydrogen bond
- ionic bond
Correct Labeling:
- Atoms and Charges:
- Label the oxygen atom (O) with a (-) charge.
- Label each hydrogen atom (H) with a (+) charge.
- Bonds:
- Between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms within a single molecule, label the bond as a polar covalent bond.
- Between hydrogen atoms of different water molecules, label the bond as a hydrogen bond.
Explanation:
- Atoms and Charges:
- In a water molecule (H₂O), oxygen (O) is more electronegative than hydrogen (H), causing it to attract electrons more strongly. This results in a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and partial positive charges on the hydrogen atoms.
- Bonds:
- Polar Covalent Bonds: These occur when two atoms share electrons unequally due to differences in electronegativity. In water, each hydrogen atom shares an electron with the oxygen atom, forming polar covalent bonds.
- Hydrogen Bonds: These are weak attractions between the hydrogen atom of one molecule and the electronegative atom (oxygen) of another molecule. Hydrogen bonds are responsible for many of water’s unique properties, such as its high boiling point relative to its molecular weight.
Understanding these labels and their placements helps in visualizing the molecular structure of water and the nature of interactions between water molecules.