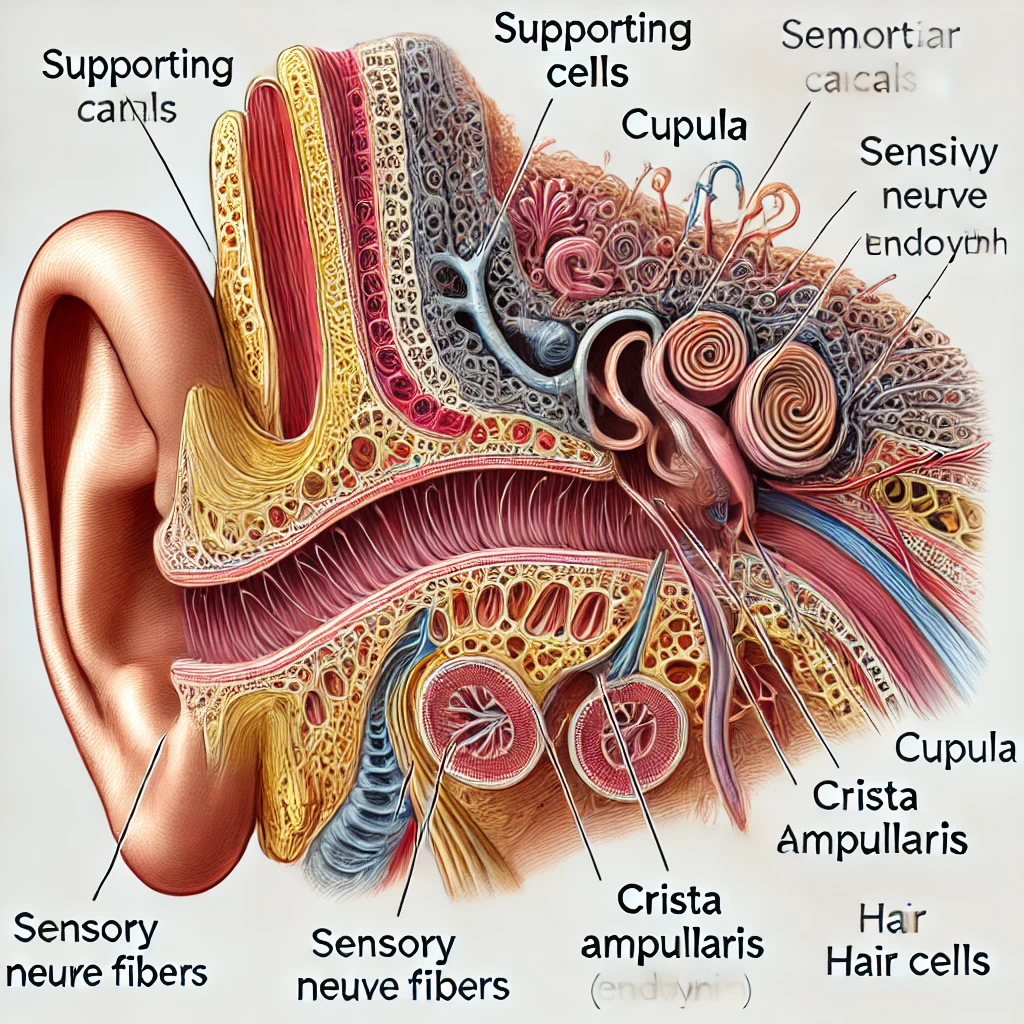
Correctly label the following anatomical features of the semicircular canals. Copyright The Meducation Pension required for reproduction or display
Supporting cells
Cupula
Sensory nerve fibers
Endolymph
Crista ampullaris
Hair cells
The correct answer and explanation is:
Labeled Anatomical Features of the Semicircular Canals
- Supporting Cells – These are non-sensory cells that provide structural and metabolic support to hair cells within the crista ampullaris.
- Cupula – A gelatinous structure that extends across the ampulla of the semicircular canals, covering the hair cells and bending in response to endolymph movement.
- Sensory Nerve Fibers – These connect the hair cells to the vestibular nerve, transmitting information about head movement to the brain.
- Endolymph – The fluid inside the semicircular canals that moves in response to head rotation, stimulating hair cells.
- Crista Ampullaris – A sensory structure within the ampulla that contains hair cells and detects rotational movements.
- Hair Cells – Sensory receptors embedded in the crista ampullaris that convert mechanical stimuli into nerve signals.
Explanation of the Semicircular Canals’ Function
The semicircular canals are part of the vestibular system, which helps maintain balance and spatial orientation. These three looped structures are filled with endolymph, a specialized fluid that moves in response to head rotations.
At the base of each semicircular canal is a widened region called the ampulla, containing a sensory organ known as the crista ampullaris. This structure houses hair cells, which have tiny projections called stereocilia embedded within the cupula, a gelatinous dome-like structure. When the head moves, endolymph shifts within the canals, deflecting the cupula and bending the hair cells. This mechanical bending converts movement into electrical nerve impulses, which are transmitted via sensory nerve fibers to the brain.
The supporting cells surround the hair cells, ensuring their health and functionality by providing mechanical stability and metabolic support.
Together, these components allow the semicircular canals to detect angular acceleration (rotational movement), helping the brain coordinate balance, posture, and eye movements. Any dysfunction in this system can lead to vertigo, dizziness, or balance disorders.
Now, I will generate an anatomical image of the semicircular canals with labeled structures.
Here is the labeled anatomical illustration of the semicircular canals, highlighting the key structures: Supporting Cells, Cupula, Sensory Nerve Fibers, Endolymph, Crista Ampullaris, and Hair Cells. Let me know if you need any modifications or additional details!