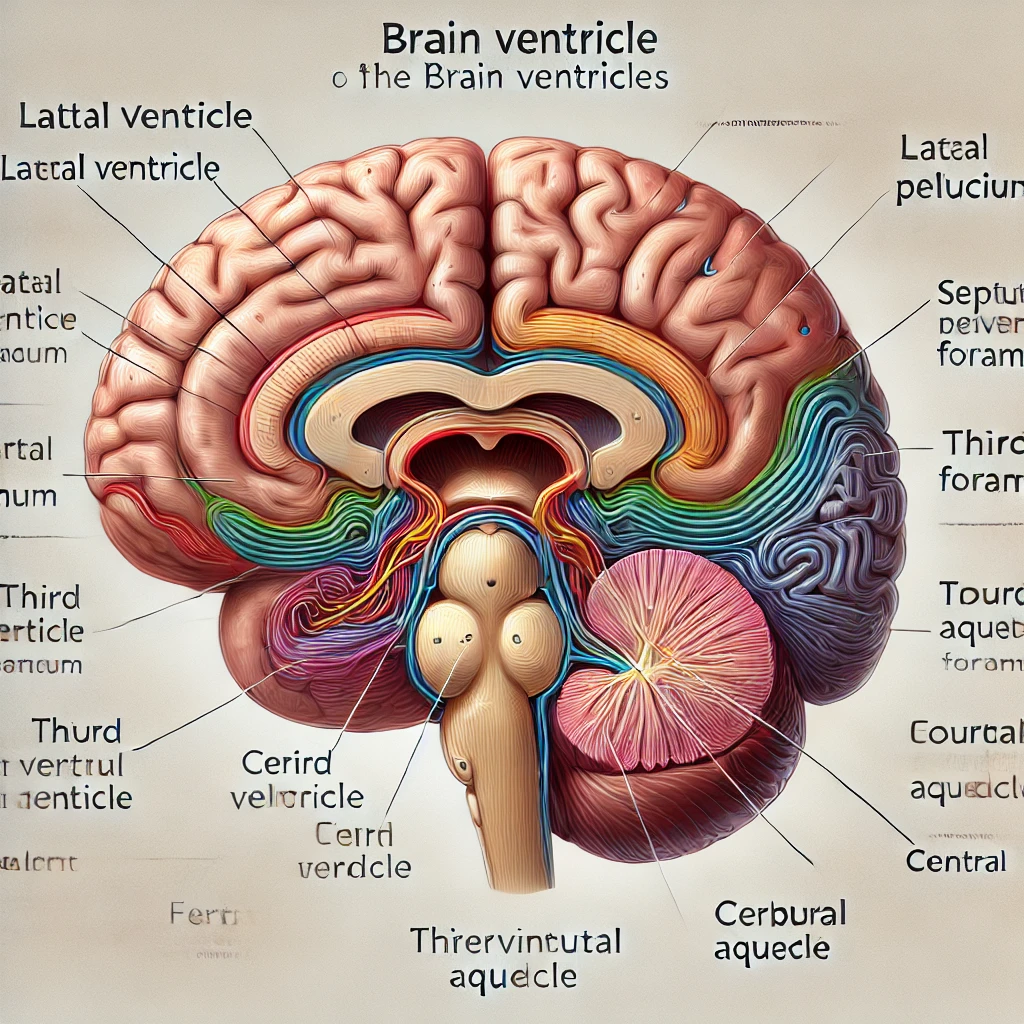
Art-labeling Activity: Figure 17.8a Part A Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Reset Help Cerebral aqueduct Central canal Lateral aperture Third ventricle Interventricular foramen Lateral ventricle II Septum pellucidum Fourth ventricle

The correct answer and explanation is:
Correct Labeling for Figure 17.8a (Part A)
- Lateral ventricle – Located in each cerebral hemisphere; the largest ventricles.
- Septum pellucidum – A thin membrane that separates the lateral ventricles.
- Interventricular foramen – A small opening that connects the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle.
- Third ventricle – A narrow, midline ventricle located in the diencephalon.
- Cerebral aqueduct – A canal that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle.
- Fourth ventricle – Located between the cerebellum and the brainstem.
- Lateral aperture – Openings in the fourth ventricle that allow cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to exit.
- Central canal – A narrow passage that runs through the spinal cord.
Explanation
The ventricular system of the brain consists of interconnected cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), playing a crucial role in protecting and nourishing the brain. The lateral ventricles are the largest and are located in each cerebral hemisphere. These ventricles are separated by the septum pellucidum, a thin membrane that prevents direct communication between them. The interventricular foramen (foramen of Monro) connects each lateral ventricle to the centrally located third ventricle, which is found in the diencephalon, near the thalamus.
The third ventricle connects to the fourth ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius), a narrow passage in the midbrain. The fourth ventricle is positioned between the cerebellum and brainstem and is crucial for CSF circulation. From the fourth ventricle, CSF exits through the lateral apertures (foramina of Luschka) and the median aperture (foramen of Magendie) into the subarachnoid space, where it surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
The central canal extends from the fourth ventricle down through the spinal cord, ensuring the distribution of CSF throughout the central nervous system. CSF provides cushioning, removes waste, and maintains chemical stability, making the ventricular system vital for brain function.
Now, I’ll generate the labeled diagram.
Here is the labeled anatomical diagram of the brain ventricles. It includes the key structures such as the lateral ventricle, septum pellucidum, third ventricle, cerebral aqueduct, fourth ventricle, and more, providing a clear visualization of their locations and connections. Let me know if you need any modifications!