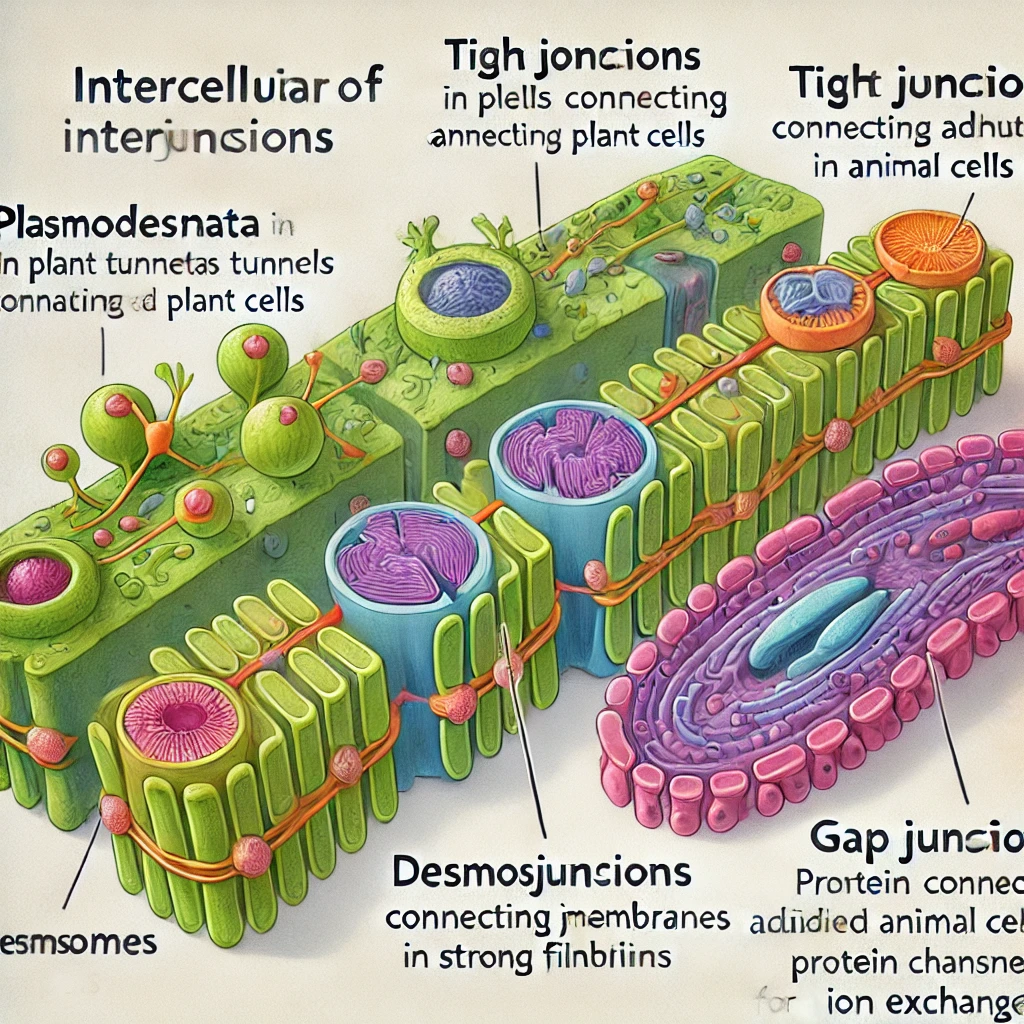
Match each type of intercellular junction with its correct description. Drag statements on the right to match the left.
plasmodesmata: channels for the exchange of substances between adjacent animal cells
tight junctions: connect animal cells to the extracellular matrix or to adjacent animal cells in one place
anchoring junctions: tunnels for the exchange of substances between adjacent plant cells
gap junctions: fuse cell membranes of adjacent animal cells, forming a barrier
The correct answer and explanation is:
Correct Matching of Intercellular Junctions
- Plasmodesmata – Tunnels for the exchange of substances between adjacent plant cells.
- Tight Junctions – Fuse cell membranes of adjacent animal cells, forming a barrier.
- Anchoring Junctions – Connect animal cells to the extracellular matrix or to adjacent animal cells in one place.
- Gap Junctions – Channels for the exchange of substances between adjacent animal cells.
Explanation
Cells in multicellular organisms communicate and maintain their structure through intercellular junctions, which are specialized structures that connect adjacent cells. These junctions play essential roles in cell adhesion, communication, and the maintenance of tissue integrity.
Plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata are microscopic channels in the cell walls of plant cells that allow direct cytoplasmic exchange between neighboring cells. These tunnels enable the transfer of nutrients, signaling molecules, and even RNA, facilitating coordination among plant cells.
Tight Junctions
Tight junctions are seal-like connections between adjacent animal cells. These junctions create an impermeable barrier that prevents the passage of molecules and ions through the space between cells. They are crucial in epithelial tissues, such as the lining of the intestines and the blood-brain barrier, where they control the movement of substances.
Anchoring Junctions
Anchoring junctions, including desmosomes and hemidesmosomes, help attach animal cells to each other or to the extracellular matrix. These junctions provide mechanical stability, especially in tissues subjected to stress, such as the skin and heart muscles.
Gap Junctions
Gap junctions are protein-based channels that link the cytoplasm of adjacent animal cells, allowing for the exchange of ions, nutrients, and signaling molecules. They are important for electrical and metabolic coordination in tissues such as the heart and nervous system.
Image Generation
Now, I’ll generate an image illustrating these intercellular junctions.
Here is a detailed scientific diagram illustrating the four types of intercellular junctions. Let me know if you need any modifications or further explanations!