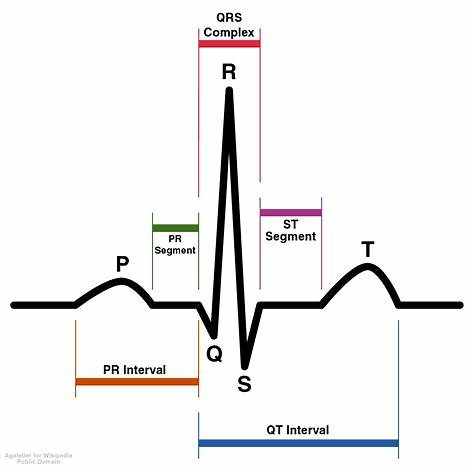
The QRS complex of the ECG tracing represents:
- A. atrial depolarization.
- B. atrial repolarization.
- C. ventricular depolarization.
- D. ventricular repolarization.
The correct answer and explanation is :
Correct Answer: C. Ventricular Depolarization
The QRS complex on an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) represents ventricular depolarization, which is the electrical activity that triggers the contraction of the ventricles. This process is essential for the heart’s function, as it allows blood to be pumped from the heart to the lungs and the rest of the body.
Understanding the QRS Complex
- Depolarization and Contraction:
- The heart’s electrical conduction system starts with the sinoatrial (SA) node, which generates an impulse that causes the atria to depolarize (P wave).
- The impulse then travels to the atrioventricular (AV) node, where it is delayed momentarily before moving through the bundle of His and Purkinje fibers.
- This electrical signal causes the ventricles to depolarize, leading to their contraction, which appears as the QRS complex on an ECG.
- Components of the QRS Complex:
- Q wave: The initial downward deflection, often small and sometimes absent.
- R wave: The first upward deflection, representing the main force of ventricular depolarization.
- S wave: A downward deflection following the R wave.
- Clinical Significance:
- A normal QRS duration is about 0.06 to 0.12 seconds.
- A widened QRS complex may indicate conditions such as bundle branch block or ventricular hypertrophy.
- A narrow QRS suggests normal conduction through the ventricles.
Why Not Other Answers?
- A (Atrial depolarization): This is represented by the P wave.
- B (Atrial repolarization): This occurs but is usually hidden within the QRS complex.
- D (Ventricular repolarization): This is shown as the T wave, not the QRS complex.
Thus, the QRS complex is specifically associated with ventricular depolarization.