Coarse, pigmented hair is called_____ , whereas most of the body hair of women and children is called___________ Most of the hair within this tube is called the___________ root, but it has a dilation at its base called the , where it derives all its nutrition from blood capillaries.
The correct answer and explanation is :
The blanks in your statement can be filled as follows:
- Coarse, pigmented hair is called terminal hair, whereas most of the body hair of women and children is called vellus hair.
- Most of the hair within this tube is called the hair root, but it has a dilation at its base called the hair bulb, where it derives all its nutrition from blood capillaries.
Explanation:
Hair on the human body varies in type, distribution, and function. Understanding these variations is essential in fields like dermatology and cosmetology.
Types of Hair:
- Terminal Hair:
- Characteristics: Terminal hair is typically long, thick, and pigmented.
- Location: Found on the scalp, legs, arms, and bodies of both males and females.
- Function: Provides protection, regulates body temperature, and serves sensory functions.
- Vellus Hair:
- Characteristics: Vellus hair is short, fine, and usually unpigmented.
- Location: Covers most of the body, except for the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- Function: Offers a light covering and assists in the evaporation of sweat.
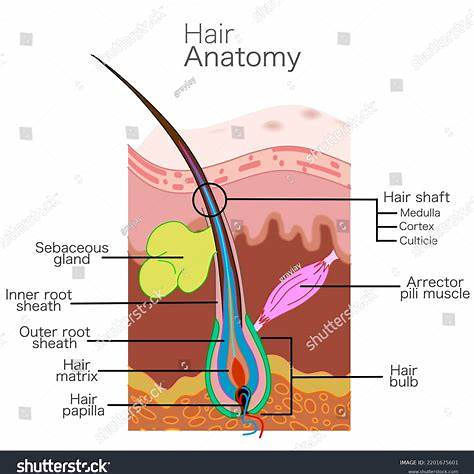
Hair Structure:
Each hair strand consists of two main parts:
- Hair Root: The portion of the hair located beneath the skin’s surface, within the hair follicle.
- Hair Shaft: The visible part of the hair that extends above the skin.
Within the hair follicle, the hair root is surrounded by several structures:
- Hair Bulb: A bulbous structure at the base of the hair root that houses the dermal papilla.
- Dermal Papilla: Contains blood vessels that supply nutrients to the growing hair, facilitating its development and health.
Image:
Understanding these aspects of hair anatomy and types aids in recognizing the diverse roles hair plays in human physiology and its variations across different individuals.