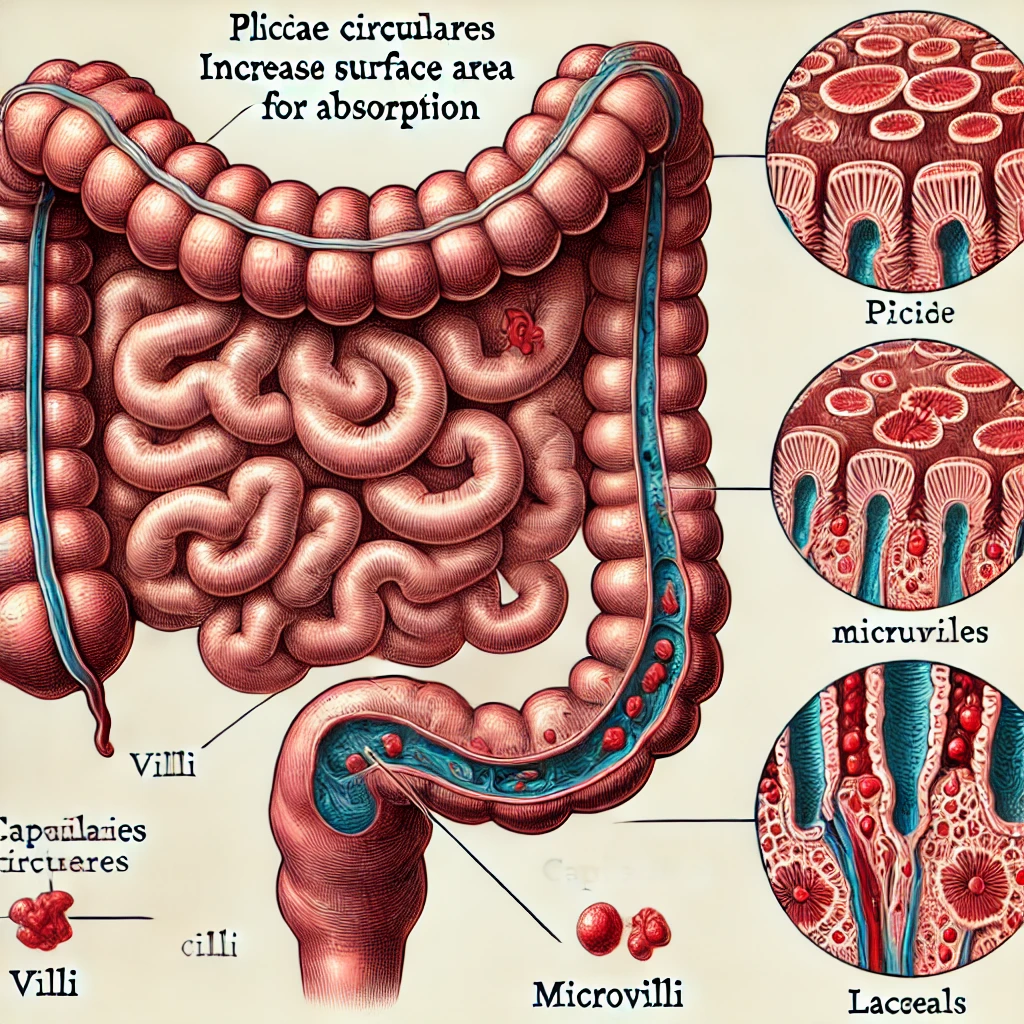
Which of these enhance the absorptive effectiveness of the small intestine?
A) the plicae circulares
C) the microvilli
B) the villi
E) All of the answers are correct.
D) intestinal movements
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct answer is:
E) All of the answers are correct.
Explanation:
The small intestine is the primary site of nutrient absorption in the digestive system. Several structural and functional adaptations enhance its absorptive effectiveness:
- Plicae Circulares (A) – These are large, circular folds of the intestinal lining that increase surface area and slow down the movement of chyme (partially digested food), allowing more time for absorption.
- Villi (B) – These are small, finger-like projections covering the inner surface of the small intestine. Each villus contains capillaries and a lacteal (lymphatic vessel), which help in absorbing nutrients like amino acids, glucose, and fatty acids.
- Microvilli (C) – Found on the surface of the epithelial cells lining the villi, microvilli form a brush border that further increases the surface area for absorption and contains digestive enzymes that aid in breaking down nutrients.
- Intestinal Movements (D) – Peristalsis and segmentation are two key movements in the small intestine. Peristalsis moves chyme forward, while segmentation mixes chyme with digestive juices, ensuring that nutrients come into contact with absorptive surfaces.
Conclusion:
Each of these adaptations contributes to the efficient absorption of nutrients. The plicae circulares, villi, and microvilli dramatically increase the surface area, while intestinal movements optimize nutrient interaction with the absorptive lining. Because all the listed factors enhance absorption, option E (“All of the answers are correct”) is the best choice.