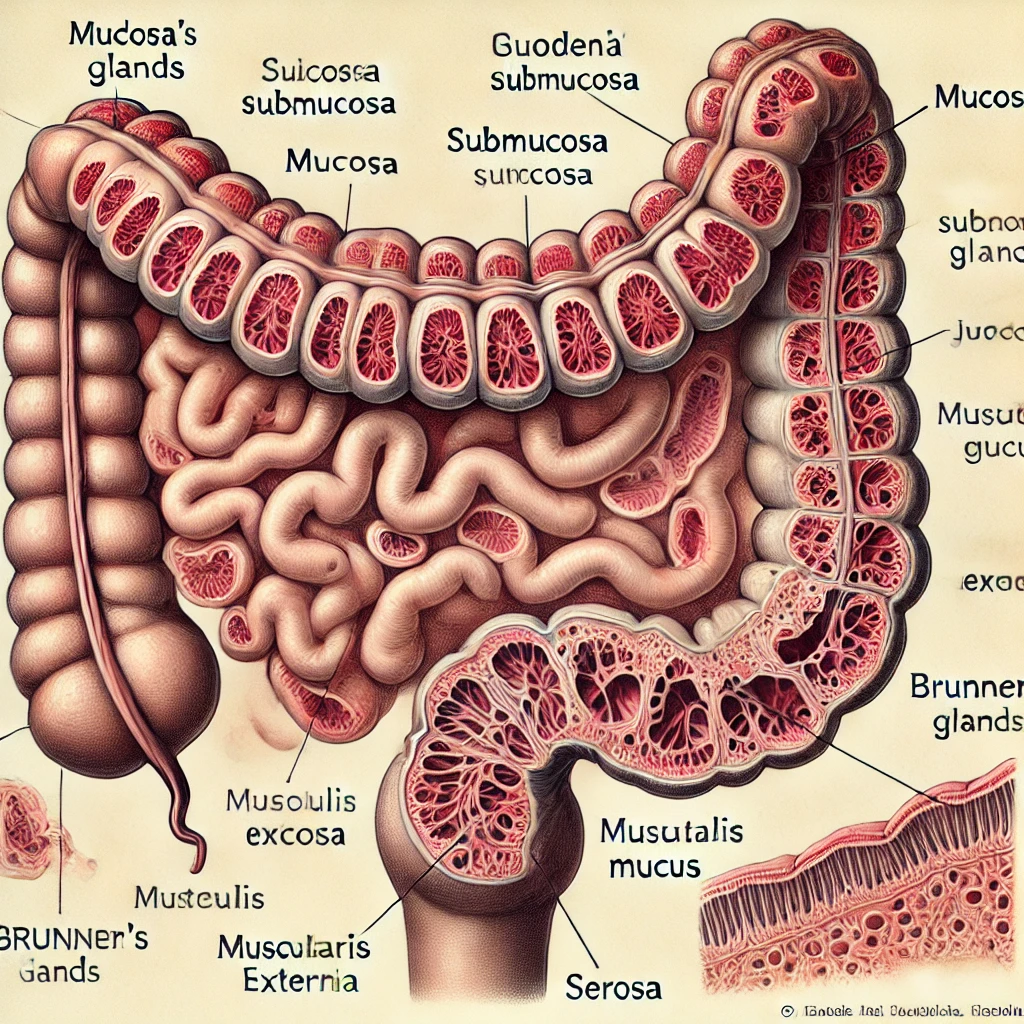
Brunner glands are characteristic of the
A) stomach.
C) jejunum.
B) duodenum.
E) colon.
D) ileum.
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct answer is:
B) Duodenum
Explanation:
Brunner’s glands are a unique and characteristic feature of the duodenum, specifically found in the submucosa of the first part of the small intestine. These branched, tubular glands secrete an alkaline mucus rich in bicarbonate, which plays a crucial role in protecting the duodenal mucosa from the acidic chyme coming from the stomach.
Functions of Brunner’s Glands:
- Neutralizing Gastric Acid – The alkaline secretion helps in buffering the acidic contents that enter the duodenum from the stomach, preventing damage to the intestinal lining.
- Providing Optimal pH for Enzymes – The secretion helps create a neutral pH environment, which is essential for the activation of pancreatic enzymes necessary for digestion.
- Lubrication – The mucus secreted by Brunner’s glands provides lubrication to facilitate the smooth movement of food.
- Antimicrobial Defense – Some secretions contain antimicrobial peptides that help prevent infections.
Histological Identification:
Brunner’s glands are located in the submucosa of the duodenum, distinguishing them from other glands found in the gastrointestinal tract. They are highly branched and tubular and secrete directly into the crypts of Lieberkühn.
Comparison with Other Intestinal Sections:
- Stomach – Contains gastric glands but lacks Brunner’s glands.
- Jejunum – Does not have Brunner’s glands; it mainly contains villi and plicae circulares.
- Ileum – Contains Peyer’s patches (lymphoid tissue) but not Brunner’s glands.
- Colon – Lacks Brunner’s glands; primarily has goblet cells for mucus secretion.
This makes Brunner’s glands a defining histological feature of the duodenum.