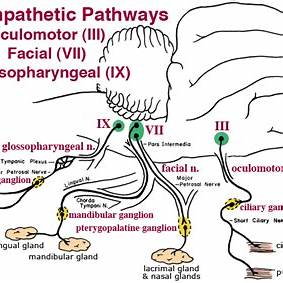
Which of these cranial nerves contains preganglionic parasympathetic fibers?
A. Optic, CNI
B. Facial, CN VII
C. Trigeminal, CN V
D. Hypoglossal, CN XII
The correct answer and explanation is :
The correct answer is:
B. Facial, CN VII
Explanation:
The cranial nerves that contain preganglionic parasympathetic fibers are part of the autonomic nervous system, specifically the parasympathetic division. These fibers originate in the brainstem and travel to ganglia before synapsing with postganglionic neurons that control various glands and smooth muscles.
There are four cranial nerves that carry preganglionic parasympathetic fibers:
- Oculomotor nerve (CN III) – Innervates the ciliary ganglion, controlling the pupil and lens for accommodation and pupillary constriction.
- Facial nerve (CN VII) – Sends fibers to the pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia, controlling lacrimal, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) – Targets the otic ganglion, influencing the parotid gland.
- Vagus nerve (CN X) – Provides extensive parasympathetic innervation to the thoracic and abdominal organs.
Why the other options are incorrect:
- A. Optic nerve (CN II) – This is purely a sensory nerve for vision and has no autonomic function.
- C. Trigeminal nerve (CN V) – While it carries autonomic fibers from other nerves to their targets, it does not contain preganglionic parasympathetic fibers itself.
- D. Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) – This nerve is entirely motor, controlling the muscles of the tongue and having no parasympathetic fibers.
Thus, the Facial nerve (CN VII) is the correct choice, as it carries preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to the pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia.
Image Representation: