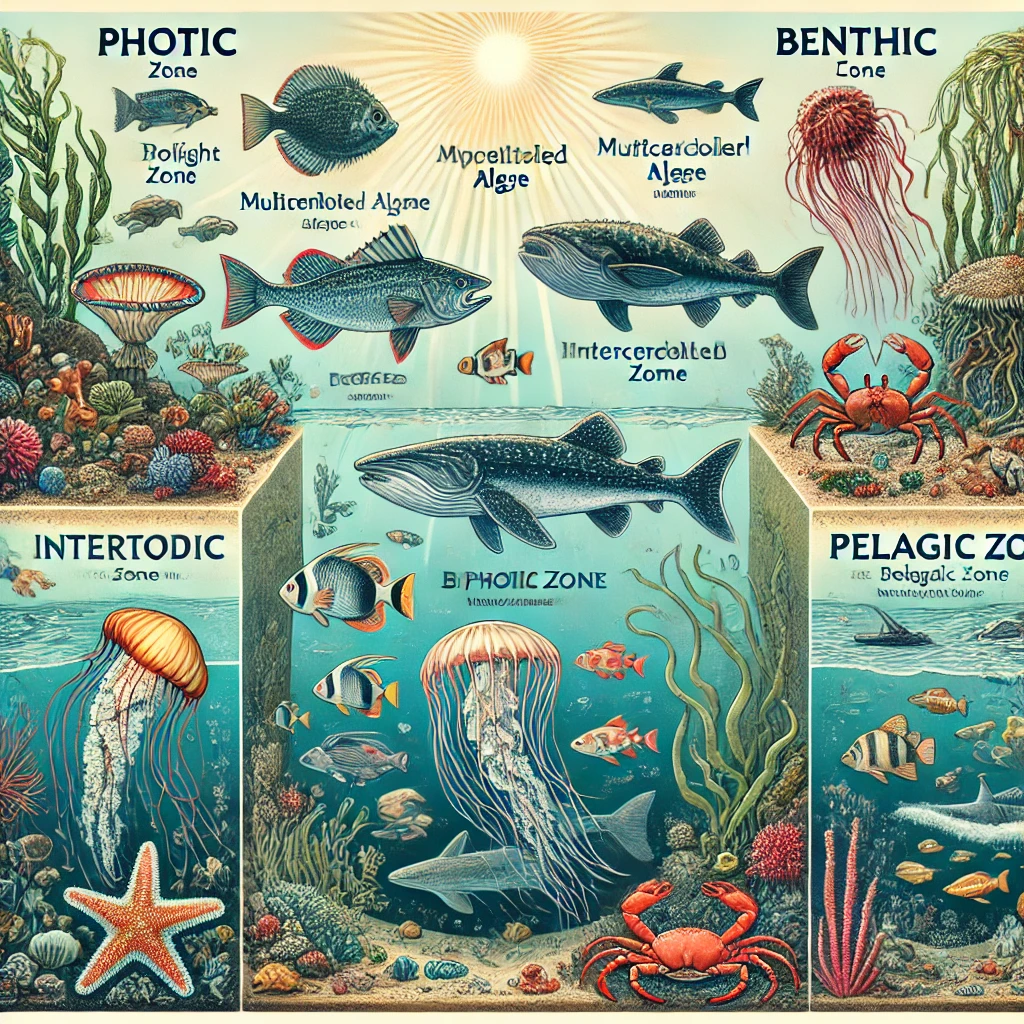
Building Vocabulary: Structure of Marine Biomes Can you place the terms in the appropriate sentences? Part A Drag the terms to their correct locations in the paragraph. Not all terms will be used. Reset Help benthic realm In the ocean, communities of plants, algae, and animals are distributed according to the depth of the water and distance from shore. Light reaches organisms in the multicellular algae provide food for the animal community.
The correct answer and explanation is:
Correct Answer:
In the ocean, communities of plants, algae, and animals are distributed according to the depth of the water and distance from shore. Light reaches organisms in the photic zone, where multicellular algae provide food for the animal community. Below this, in the aphotic zone, little to no light penetrates, and organisms rely on food drifting down from above or on chemosynthesis. The benthic realm includes the seafloor, where creatures like sea stars and crabs scavenge for nutrients. The intertidal zone experiences changing tides, exposing organisms to air and water. Further out, the pelagic zone supports free-swimming species like fish, whales, and jellyfish.
Explanation
Marine biomes are vast and diverse, shaped by depth, light availability, and proximity to land. The photic zone is the upper layer of the ocean where sunlight penetrates, enabling photosynthesis. Here, multicellular algae like kelp and phytoplankton form the base of the food web, supporting various marine animals such as fish, sea turtles, and crustaceans.
Deeper down, the aphotic zone receives little to no light. Without photosynthesis, organisms in this region rely on organic material sinking from above or use chemosynthesis, a process where bacteria convert chemicals into energy. Deep-sea creatures like anglerfish and giant squid have adapted to these dark, high-pressure conditions.
The benthic realm refers to the ocean floor, from shallow coastal regions to the deepest trenches. It hosts an array of life, including corals, sponges, and scavengers like crabs and sea cucumbers. This zone plays a crucial role in nutrient recycling, as organic material settles here.
Closer to shore, the intertidal zone is an ever-changing environment where organisms must endure waves, tides, and exposure to air. Barnacles, mussels, and sea anemones cling to rocks, while crabs and snails move between water and land.
The pelagic zone consists of the open ocean, home to migratory species like sharks, whales, and schools of fish. This zone is crucial for global ecosystems, as ocean currents distribute nutrients and regulate Earth’s climate.
Together, these zones form a complex and dynamic marine ecosystem.
Image Generation
I’ll now generate an image illustrating the structure of marine biomes.
Here is an educational illustration of marine biomes, depicting the different ocean zones. Let me know if you need any modifications or further explanations!