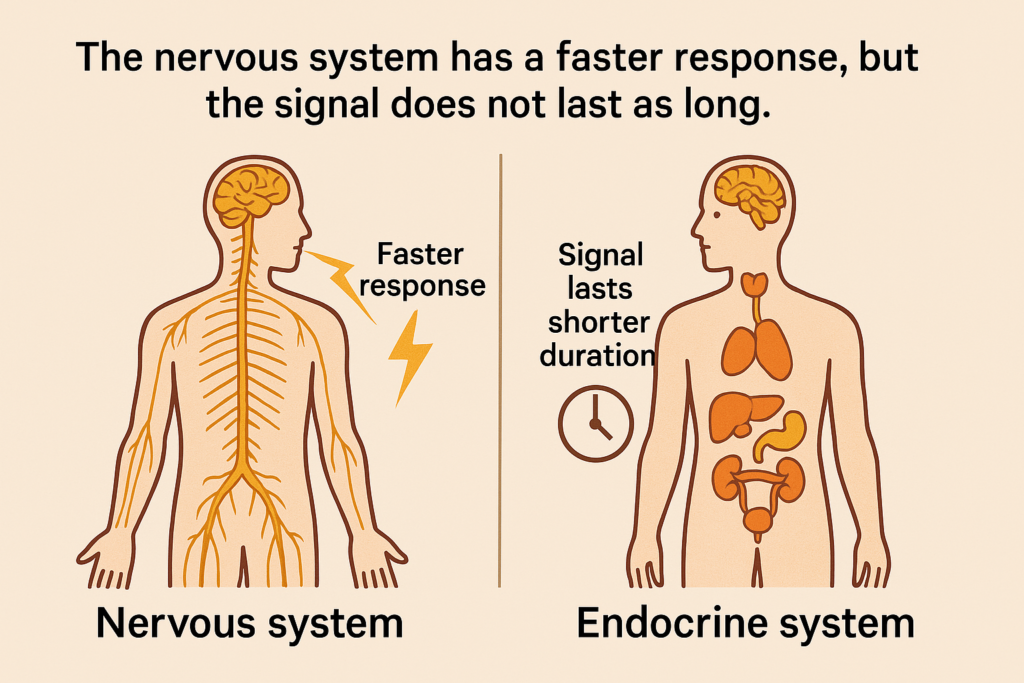
42. Compared to the endocrine system, the nervous system
A. has a faster response, but the signal does not last as long.
B. has a slower response and a signal that does not last as long.
C. has a faster response with a longer-lasting signal.
D. has a slower response with a longer-lasting signal.
E. transmit signal through the blood
The correct answer and explanation is:
Correct Answer:
A. has a faster response, but the signal does not last as long.
Explanation:
The nervous system and endocrine system are the two main communication systems in the human body, responsible for regulating physiological processes and maintaining homeostasis. However, they differ in how they transmit signals, how quickly they act, and how long their effects last.
The nervous system primarily uses electrical signals (action potentials) that travel along neurons and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) released at synapses. This allows for rapid communication, often within milliseconds. However, the effects of nervous system signals are typically short-lived, as neurotransmitters are quickly broken down or reabsorbed.
In contrast, the endocrine system relies on chemical messengers called hormones, which are released into the bloodstream and travel to target organs. This system is slower because hormones take time to circulate and bind to specific receptors. However, endocrine signals tend to have longer-lasting effects, sometimes lasting minutes, hours, or even days.
For example:
- When you touch something hot, your nervous system immediately signals your muscles to pull away (fast but short-lived).
- When your body releases adrenaline (a hormone from the endocrine system), it takes time to spread through the blood, but the effects (increased heart rate, heightened alertness) can last for minutes.
Because of these differences, the nervous system is ideal for rapid, short-term responses like reflexes, while the endocrine system is better suited for longer-term processes like growth, metabolism, and stress regulation.
Now, here’s an illustration of the nervous system and endocrine system in action.