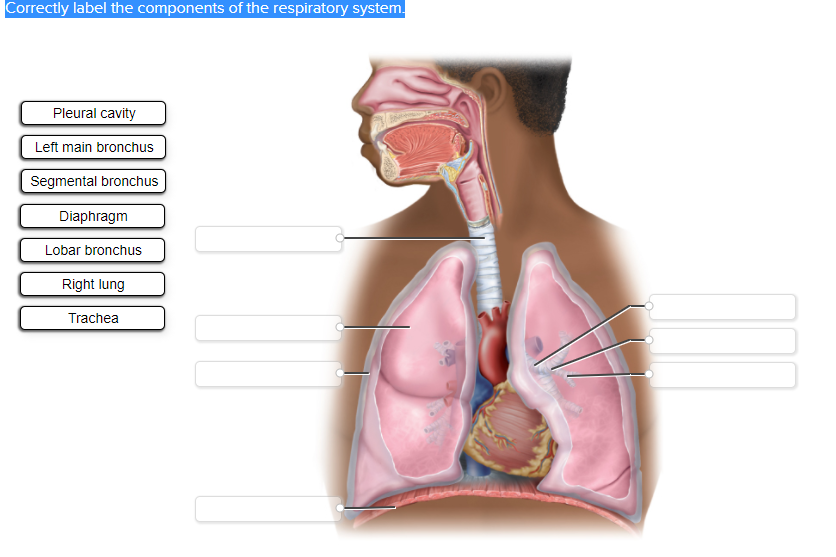
Correctly label the components of the respiratory system.
Pleural cavity
Left main bronchus
Segmental bronchus
Diaphragm
Lobar bronchus
Right lung
Trachea
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the correctly labeled components of the respiratory system based on the provided diagram:
- Trachea – Topmost blank label (central white tube leading down from throat)
- Left main bronchus – Second blank on the left side (divides from the trachea into the left lung)
- Lobar bronchus – Topmost blank on the right side (branching within the lung)
- Segmental bronchus – Middle blank on the right side (smaller branches inside the lung)
- Right lung – Bottom blank on the right side (entire lung structure)
- Pleural cavity – Middle blank on the left side (space between lungs and chest wall)
- Diaphragm – Bottom blank on the left side (curved muscular structure at the bottom)
The respiratory system is essential for gas exchange, allowing oxygen to enter the blood and carbon dioxide to exit. The system begins at the trachea, a tube reinforced with cartilage that extends from the larynx and branches into the bronchi. It is responsible for directing air into the lungs and is lined with cilia and mucus to trap particles.
The left main bronchus is a major airway that splits from the trachea and carries air into the left lung. Inside the lungs, the bronchi subdivide into lobar bronchi, each serving a specific lobe of the lung. These further divide into segmental bronchi, which supply bronchopulmonary segments—smaller functional units of the lung. This branching increases the surface area for efficient gas exchange.
The right lung, seen on the diagram’s right side (from the patient’s perspective), consists of three lobes and is larger than the left lung due to the positioning of the heart. Surrounding each lung is the pleural cavity, a thin fluid-filled space that allows the lungs to move smoothly during breathing and maintains lung expansion by creating negative pressure.
At the base of the system is the diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle that contracts and flattens during inhalation, increasing thoracic volume and drawing air into the lungs. Relaxation of the diaphragm leads to exhalation.
Understanding the anatomy and function of these components is critical for diagnosing and treating respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, or pneumonia.
