Answer the following questions about the amino acid whose Fischer projection formula is
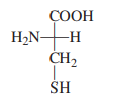
a. Is it a D-amino acid or an L-amino acid? b. Is it a nonpolar or polar amino acid? c. Is it an essential or nonessential amino acid? d. Is it a standard or nonstandard amino acid?
At room temperature, amino acids are solids with relatively high decomposition points. Explain why.
At room temperature, most amino acids are not very soluble in water. Explain why.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The amino acid shown in the Fischer projection is cysteine, with the structure:
COOH
|
H2N—C—H
|
CH2
|
SH
a. Is it a D-amino acid or an L-amino acid?
Answer: L-amino acid
Explanation: In the Fischer projection, if the amino group (-NH₂) is on the left of the chiral carbon, the amino acid is in the L-configuration. This matches the configuration of naturally occurring amino acids in proteins.
b. Is it a nonpolar or polar amino acid?
Answer: Polar amino acid
Explanation: Cysteine contains a thiol (-SH) group, which can form hydrogen bonds and is moderately polar. It can participate in redox reactions (forming disulfide bonds), contributing to its polarity.
c. Is it an essential or nonessential amino acid?
Answer: Nonessential amino acid
Explanation: Cysteine is considered nonessential because the human body can synthesize it, mainly from methionine (an essential amino acid).
d. Is it a standard or nonstandard amino acid?
Answer: Standard amino acid
Explanation: Cysteine is one of the 20 standard amino acids used in protein biosynthesis.
Why are amino acids solids with high decomposition points at room temperature?
Amino acids exist in their zwitterionic form at room temperature, where the amino group is protonated (-NH₃⁺) and the carboxyl group is deprotonated (-COO⁻). These opposite charges result in strong electrostatic (ionic) interactions between molecules, much like salts. These strong interactions require a lot of energy to overcome, giving amino acids high melting (decomposition) points and making them solids at room temperature.
Why are most amino acids not very soluble in water at room temperature?
While amino acids are polar, their solubility in water is limited due to the zwitterionic nature, which promotes strong intermolecular attractions. These interactions can make it energetically unfavorable for water molecules to break apart amino acid clusters, especially for amino acids with nonpolar side chains. Additionally, the crystalline structure in the solid state also reduces solubility, as dissolving requires disrupting a stable ionic lattice.
Summary:
Cysteine is an L-form, polar, nonessential, and standard amino acid. Amino acids are solids with high decomposition points due to strong ionic interactions in their zwitterionic form. Limited solubility in water arises from strong intermolecular forces and the nature of their side chains.
