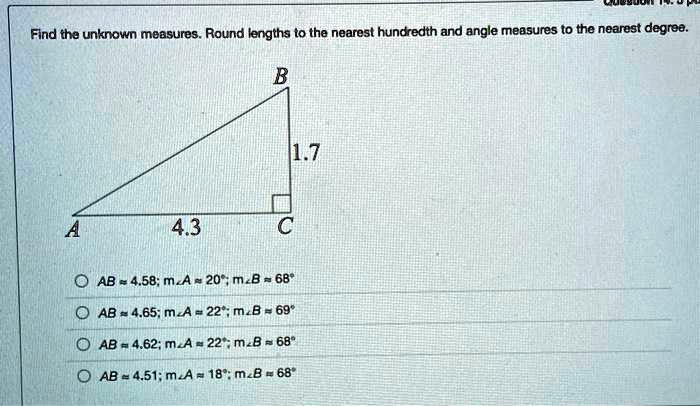
Find tha unknown measures. Round langths to Ihe – nearest hundredth and angle measures to the nearest degroe. 4.3 AB = 4.58; MA = 20 ; m_B = 68″ AB = 4.65; m_A =22;m.B = 69″ AB = 4.62; mA = 22 ; m_B = 68″ AB = 4.51;m.A =18: m_8 = 68″
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct answer is AB = 4.62, m∠A = 22°, m∠B = 68°.
To determine these values, we use the Pythagorean theorem and trigonometric functions. Given the right triangle ABC, where AC is 4.3 and BC is 1.7, we find the hypotenuse AB by applying the Pythagorean theorem:
AB² = AC² + BC² AB = √(4.3² + 1.7²) AB = √(18.49 + 2.89) AB = √21.38 AB ≈ 4.62
Next, we determine the angle A using the tangent function:
tan(A) = BC / AC A = arctan(1.7 / 4.3) A ≈ arctan(0.3953) A ≈ 22°
Since the sum of angles in a triangle is 180° and one angle is 90°, we calculate angle B:
B = 90° – A B ≈ 90° – 22° B ≈ 68°
Now, for the explanation:
The Pythagorean theorem is a fundamental relationship in right triangles that states the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides equals the square of the hypotenuse. Using this theorem, we accurately determine AB as approximately 4.62.
To calculate angles A and B, trigonometric ratios such as tangent are useful. The tangent function is defined as the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. By using the inverse tangent function, we find that angle A is approximately 22°. Since the angles of a triangle sum to 180°, we subtract the known values to determine that angle B is approximately 68°.
Applying these mathematical principles ensures precise calculations for both side lengths and angle measures, leading to the correct answer.
