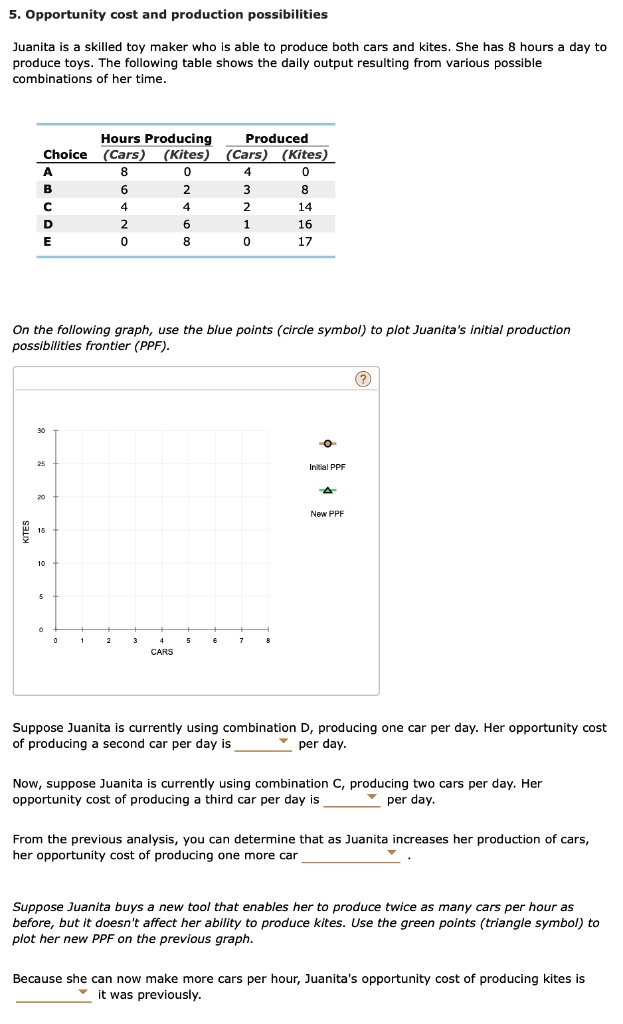
Opportunity cost and production possibilities Juanita is a skilled toy maker who is able to produce both cars and kites. She has 8 hours a day to produce toys. The following table shows the daily output resulting from various possible combinations of her time. Hours Producing Produced Choice (Cars) (Kites) (Cars) (Kites) A 8 0 4 0 B 6 2 3 8 C 4 4 2 14 D 2 6 1 16 E 0 8 0 17 On the following graph, use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot Juanita’s initial production possibilities frontier (PPF). CARS Initial PPF A New PPF Suppose Juanita is currently using combination D, producing one car per day. Her opportunity cost of producing a second car per day is per day. Now, suppose Juanita is currently using combination C, producing two cars per day. Her opportunity cost of producing a third car per day is ?per day. From the previous analysis, you can determine that as Juanita increases her production of cars, her opportunity cost of producing one more car Suppose Juanita buys a new tool that enables her to produce twice as many cars per hour as before, but it doesn’t affect her ability to produce kites. Use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot her new PPF on the previous graph. Because she can now make more cars per hour, Juanita’s opportunity cost of producing kites is it was previously
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Opportunity Cost Calculations:
- At Combination D (1 Car, 16 Kites)
- Moving from D (1 car, 16 kites) to C (2 cars, 14 kites), she sacrifices 2 kites for an additional car.
- Opportunity cost of producing a second car = 2 kites per day.
- At Combination C (2 Cars, 14 Kites)
- Moving from C (2 cars, 14 kites) to B (3 cars, 8 kites), she sacrifices 6 kites for one more car.
- Opportunity cost of producing a third car = 6 kites per day.
- General Trend in Opportunity Cost
- As Juanita increases car production, she gives up more kites each time.
- Her opportunity cost of producing one more car increases.
Impact of the New Tool:
- Juanita’s ability to produce cars doubles while her kite-making capacity remains unchanged.
- Previously, she could make 4 cars in 8 hours. Now, she can make 8 cars in the same time.
- Her new PPF shifts outward for cars, but remains unchanged for kites.
- Since she can now produce more cars without affecting kite output, the opportunity cost of producing kites increases compared to before.
Explanation:
Opportunity cost measures the trade-off between two goods when resources are limited. Juanita experiences increasing opportunity costs in car production, meaning each additional car requires sacrificing more kites. The new tool alters this dynamic by increasing car production efficiency, which makes kites relatively more expensive in terms of forgone cars. This shift in the PPF illustrates how technological improvements impact trade-offs in production.
