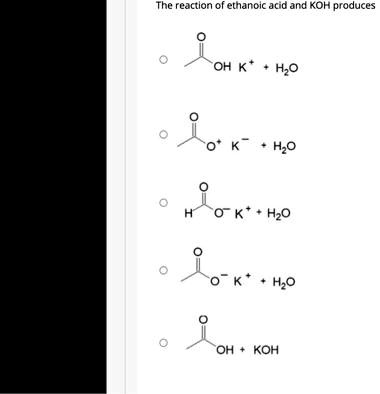
In a reaction between ethanoic acid and KOH, it produces OH- and K+ ions. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is: CH3COOH + KOH → CH3COOK + H2O
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The reaction between ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH) is a neutralization reaction, where an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water. The correct balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
CH3COOH + KOH → CH3COOK + H2O
Ethanoic acid is a weak acid, meaning it only partially dissociates in solution. Potassium hydroxide is a strong base, meaning it completely dissociates into potassium (K+) and hydroxide (OH-) ions. When the two react, the hydroxide ion (OH-) from KOH accepts a proton (H+) from ethanoic acid, forming water (H2O). The remaining acetate ion (CH3COO-) combines with the potassium ion (K+) to form potassium acetate (CH3COOK), which is a salt.
This reaction illustrates an acid-base neutralization, where a proton transfer occurs. The reaction is exothermic, releasing heat as water and potassium acetate form. Since ethanoic acid is weak, it does not fully ionize in solution. However, when it reacts with a strong base like KOH, it undergoes complete neutralization, forming a fully soluble salt.
Potassium acetate has several practical applications. It is used in the food industry as a preservative and acidity regulator. In the pharmaceutical industry, it serves as a buffering agent. Additionally, potassium acetate is used in de-icing solutions for roads and airport runways because it is less corrosive than traditional salts like sodium chloride.
The reaction follows the principles of stoichiometry, meaning the atoms and charges are conserved. The balanced equation ensures that one mole of ethanoic acid reacts with one mole of potassium hydroxide to form one mole of potassium acetate and one mole of water. This reaction also demonstrates the concept of conjugate acid-base pairs, as ethanoic acid and acetate ion form a conjugate pair. Water and hydroxide ion similarly form another conjugate pair, highlighting the interaction between acid and base components.
