Structural Formula for Propene H
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
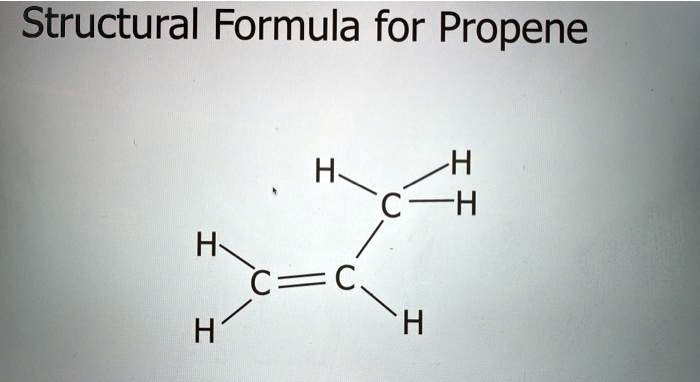
The image you provided shows the structural formula for propene (C₃H₆), an alkene with three carbon atoms and a double bond between the first and second carbon atoms.
In the structural formula:
- There are three carbon atoms (C) connected by single bonds, with the second carbon atom also double-bonded to the third carbon atom.
- Each carbon is bonded to hydrogen atoms (H) to satisfy its four bonds.
Here’s how the bonds work:
- The first carbon (C₁) is bonded to two hydrogen atoms (H) and has a single bond to the second carbon (C₂).
- The second carbon (C₂) is bonded to one hydrogen atom, has a double bond to the third carbon (C₃), and is bonded to the first carbon (C₁).
- The third carbon (C₃) is bonded to two hydrogen atoms (H) and has a double bond with the second carbon (C₂).
The structural formula of propene is C₃H₆, and it can be represented as:
CH₂=CH-CH₃
In this representation:
- “CH₂” means the carbon is bonded to two hydrogens.
- “=CH” means the carbon is double-bonded to another carbon.
- “CH₃” means the carbon is bonded to three hydrogens.
Propene is an important intermediate in the production of polypropylene and other chemicals. The double bond makes it a member of the alkene family, which is characterized by at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
