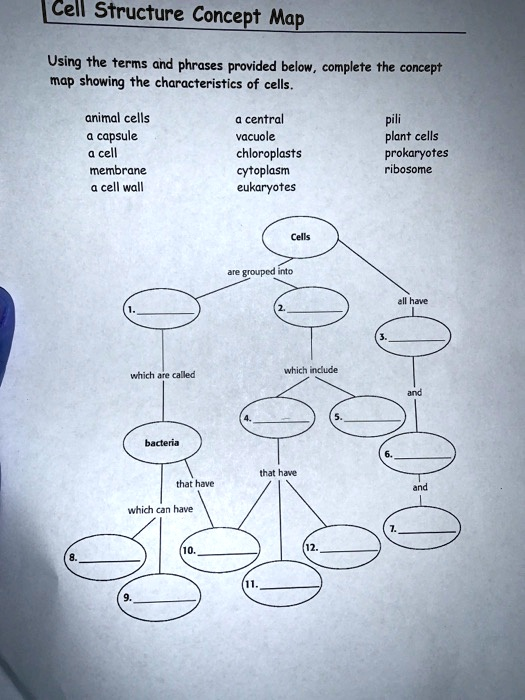
Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the characteristics of cells. animal cells capsule cell membrane cell wall central vacuole chloroplasts cytoplasm eukaryotes plant cells prokaryotes ribosome
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
To complete the concept map based on the terms provided, here’s the completed structure with appropriate explanations:
- Bacteria
- Bacteria are a type of prokaryotic cell. They can exist as single-celled organisms or in groups, and they lack membrane-bound organelles.
- Eukaryotes
- Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, distinguishing them from prokaryotes. Eukaryotes can be plant cells or animal cells.
- A cell membrane
- All cells, whether prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have a cell membrane, which controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm
- The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance inside the cell membrane. It is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and houses various organelles.
- Ribosomes
- Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. They are found floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- A capsule
- Some bacteria, particularly prokaryotic cells, have a capsule that surrounds the cell wall. This capsule offers protection and can help bacteria evade the immune system.
- A cell wall
- Plant cells and bacteria have a cell wall, which provides structural support and protection. In plants, the cell wall is made of cellulose, while in bacteria, it is made of peptidoglycan.
- Animal cells
- Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that lack a cell wall and have a more flexible shape due to the presence of only a cell membrane.
- A central vacuole
- Plant cells have a large central vacuole that stores water and other substances, providing structural support to the cell.
- Chloroplasts
- Chloroplasts are found in plant cells and some eukaryotic algae. They contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy.
- Prokaryotes
- Prokaryotic cells are simpler cells that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. Bacteria are the most common type of prokaryotic organisms.
- Plant cells
- Plant cells are a type of eukaryotic cell that has a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a central vacuole, which are absent in animal cells.
Explanation:
Cells can be categorized into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes, like bacteria, are simpler and lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes, such as animal and plant cells, contain a nucleus and more complex structures. Both cell types have some common features, such as a cell membrane and cytoplasm. However, eukaryotic plant cells have unique components like chloroplasts, a central vacuole, and a cell wall, which provide additional functions like photosynthesis and structural support. Animal cells, by contrast, do not have these structures but instead have flexible cell membranes.
