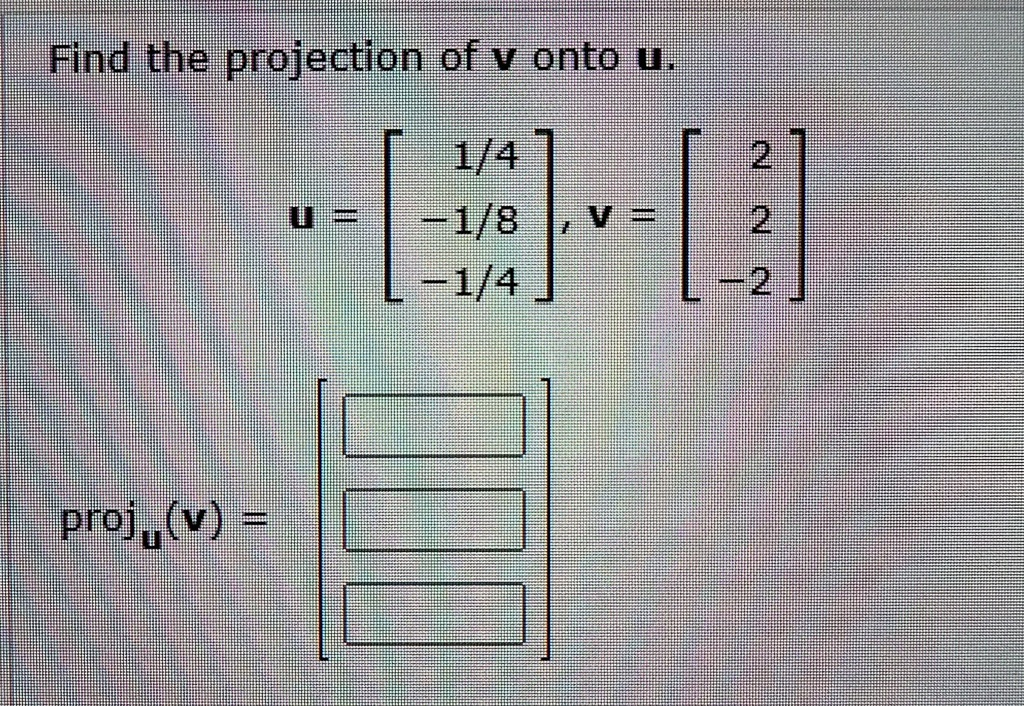
Find the projection of v onto u.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here is the correct answer:
proj_u(v)
[ 4/3 ]
[-2/3 ]
[-4/3 ]Explanation:
To find the projection of a vector v onto another vector u, we use the formula:
proj_u(v) = ( (v · u) / (u · u) ) * u
This formula calculates a scalar value (the fraction part) and then multiplies it by the vector u. The resulting vector is the component of v that lies in the direction of u. The calculation can be broken down into three main steps.
Step 1: Calculate the dot product of v and u (v · u).
The dot product is found by multiplying the corresponding components of the two vectors and then summing the results.
v = [2, 2, -2]
u = [1/4, -1/8, -1/4]
v · u = (2 * 1/4) + (2 * -1/8) + (-2 * -1/4)
v · u = 2/4 – 2/8 + 2/4
v · u = 1/2 – 1/4 + 1/2
v · u = 1 – 1/4 = 3/4
Step 2: Calculate the dot product of u with itself (u · u).
This is equivalent to finding the squared magnitude of u.
u · u = (1/4 * 1/4) + (-1/8 * -1/8) + (-1/4 * -1/4)
u · u = 1/16 + 1/64 + 1/16
To add these fractions, we find a common denominator, which is 64.
u · u = 4/64 + 1/64 + 4/64
u · u = 9/64
Step 3: Calculate the projection.
Now, we substitute the values from the first two steps into the projection formula.
proj_u(v) = ( (3/4) / (9/64) ) * u
First, we simplify the scalar fraction. Dividing by a fraction is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal.
Scalar = (3/4) * (64/9) = (3 * 64) / (4 * 9) = 192 / 36
Simplifying this fraction gives 16/3.
Finally, we multiply this scalar by the vector u.
proj_u(v) = (16/3) * [1/4, -1/8, -1/4]
proj_u(v) = [ (16/3) * (1/4), (16/3) * (-1/8), (16/3) * (-1/4) ]
proj_u(v) = [ 16/12, -16/24, -16/12 ]
Simplifying each component gives the final answer:
proj_u(v) = [ 4/3, -2/3, -4/3 ]
