A C. B Where is the center of mass of a uniform half-circle in the above
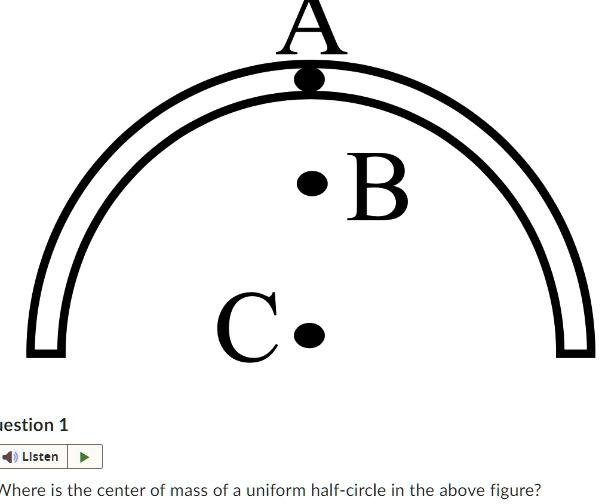
The correct answer is B.
The center of mass is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. In simpler terms, it is the “balance point” of an object. To determine the location of the center of mass for the uniform half-circle shown, we can use principles of symmetry and mass distribution.
First, consider the symmetry of the object. The uniform half-circle is perfectly symmetrical about a vertical line that passes through its highest point, A, and the center of the circle from which the arc is taken. Because the mass is distributed uniformly, the center of mass must lie somewhere along this line of symmetry. This means that points A, B, and C are all potential candidates, as they are all located on this central axis.
Next, we must consider where the mass is located. The center of mass is the average position of all the mass in the object. For a curved object like this arc, the center of mass is not located on the object itself. Imagine trying to balance the arc on your fingertip. You could not balance it by placing your finger at point A on the top of the curve. The mass distributed on both sides would cause it to fall. Therefore, the balance point must be located inside the space enclosed by the arc. This eliminates point A as a possibility.
Now we must choose between points B and C. The object is a hollow arc, not a solid, filled-in semicircle. This means all of its mass is concentrated along the curved line. This distribution pulls the center of mass higher up, closer to the arc itself, compared to where it would be for a solid shape. If the object were a solid semicircular plate, its mass would be spread out over the entire area, and its center of mass would be located lower down, closer to the flat bottom edge, at a position more like C. Since the figure depicts a line arc, its center of mass is found at point B, which represents the higher balance point characteristic of a hollow semicircular shape
