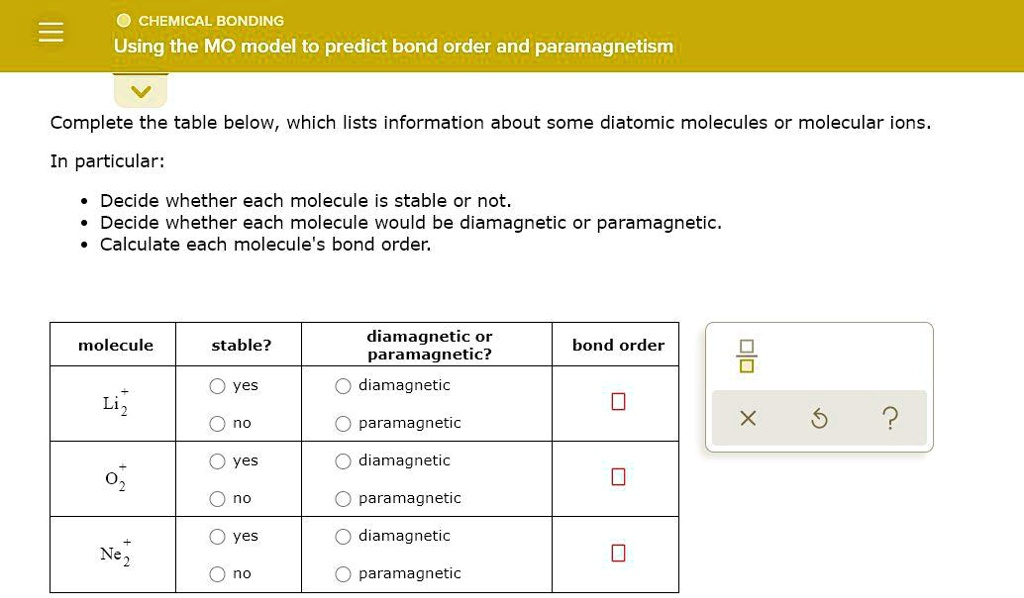
CHEMICAL BONDING Using the MO model to predict bond order and paramagnetism Complete the table below, which lists information about some diatomic molecules or molecular ions. In particular: Decide whether each molecule is stable or not Decide whether each molecule would be diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Calculate each molecule’s bond order; diamagnetic or paramagnetic? molecule stable? bond order yes diamagnetic no paramagnetic 2 yes diamagnetic paramagnetic yes diamagnetic Ne2 no paramagnetic Liz
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Completed Table:
| molecule | stable? | diamagnetic or paramagnetic? | bond order |
| Li₂⁺ | yes | paramagnetic | 0.5 |
| O₂⁺ | yes | paramagnetic | 2.5 |
| Ne₂⁺ | yes | paramagnetic | 0.5 |
Explanation:
To determine the properties of these diatomic species, we use Molecular Orbital (MO) theory. The stability, magnetic properties, and bond order are derived from the species’ MO electron configuration.
- Stability: A molecule or ion is considered stable if its bond order is greater than zero (BO > 0).
- Bond Order (BO): Calculated as BO = ½ (Number of electrons in bonding MOs – Number of electrons in antibonding MOs).
- Magnetic Properties: A species is paramagnetic if it has one or more unpaired electrons and is diamagnetic if all its electrons are paired.
Analysis of each species:
- Li₂⁺: A lithium (Li) atom has 3 electrons. The Li₂⁺ ion has (2 × 3) – 1 = 5 electrons. Its MO configuration is (σ₁s)²(σ*₁s)²(σ₂s)¹.
- Bond Order: There are 3 electrons in bonding orbitals (σ₁s, σ₂s) and 2 in antibonding orbitals (σ*₁s). BO = ½ (3 – 2) = 0.5.
- Stability: Since the bond order is 0.5 (> 0), Li₂⁺ is stable.
- Magnetism: The σ₂s orbital contains one unpaired electron, making Li₂⁺ paramagnetic.
- O₂⁺: An oxygen (O) atom has 8 electrons. The O₂⁺ ion has (2 × 8) – 1 = 15 electrons. Its valence electron MO configuration is (σ₂s)²(σ₂s)²(σ₂p)²(π₂p)⁴(π₂p)¹.
- Bond Order: There are 8 valence electrons in bonding orbitals (σ₂s, σ₂p, π₂p) and 3 in antibonding orbitals (σ₂s, π₂p). BO = ½ (8 – 3) = 2.5.
- Stability: With a bond order of 2.5, O₂⁺ is stable.
- Magnetism: The π*₂p antibonding orbitals have one unpaired electron, making O₂⁺ paramagnetic.
- Ne₂⁺: A neon (Ne) atom has 10 electrons. The Ne₂⁺ ion has (2 × 10) – 1 = 19 electrons. Its valence electron MO configuration is (σ₂s)²(σ₂s)²(σ₂p)²(π₂p)⁴(π₂p)⁴(σ*₂p)¹.
- Bond Order: There are 8 valence electrons in bonding orbitals and 7 in antibonding orbitals. BO = ½ (8 – 7) = 0.5.
- Stability: The bond order is 0.5, so Ne₂⁺ is predicted to be stable, unlike the Ne₂ molecule which has a bond order of 0.
- Magnetism: There is one unpaired electron in the σ*₂p orbital, making Ne₂⁺ paramagnetic.
