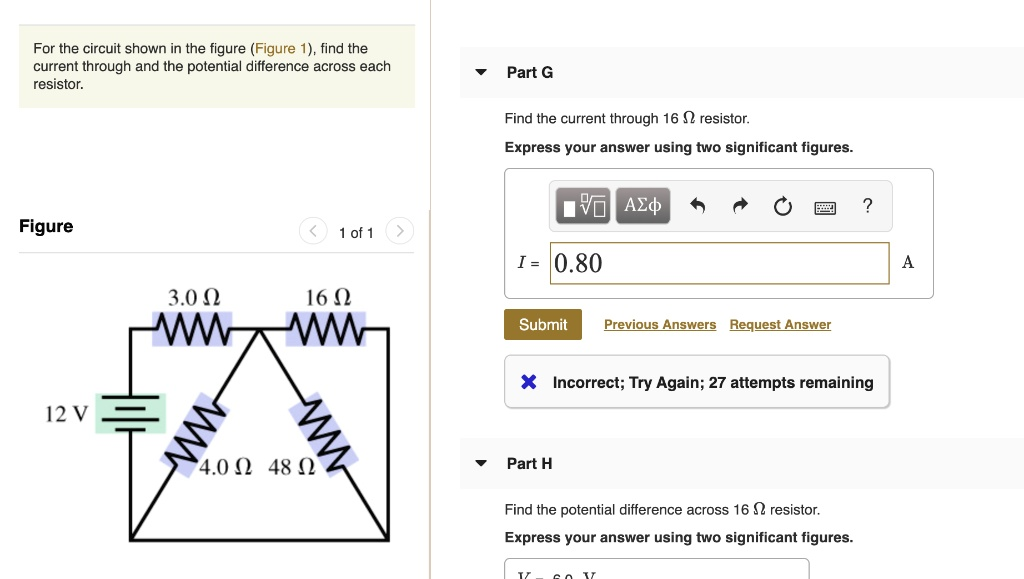
For the circuit shown in the figure (Figure 1), find the current through and the potential difference across each resistor. Part G Find the current through 16
resistor. Express your answer using two significant figures. Figure < 1 of 1 >
3.0
16
12 V 4.0
48
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Incorrect; Try Again; 27 attempts remaining Part H Find the potential difference across 16
resistor. Express your answer using two significant figures.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Of course. Here are the correct answers and a step-by-step explanation for solving this circuit problem.
Correct Answers
Part G: Find the current through the 16 Ω resistor.
I = 0.56 A
Part H: Find the potential difference across the 16 Ω resistor.
V = 9.0 V
Explanation
This circuit cannot be simplified using basic series and parallel rules alone. The arrangement of the 3.0 Ω, 4.0 Ω, and 16 Ω resistors forms a delta (Δ) configuration, which requires a more advanced technique like a Delta-Wye (Δ-Y) transformation or using Kirchhoff’s Laws. The Δ-Y transformation is often the most straightforward method.
1. Identify the Nodes and the Delta Configuration
First, let’s label the important nodes (junctions) in the circuit:
- J1: The junction connected to the positive terminal of the 12 V battery, the 3.0 Ω resistor, and the 4.0 Ω resistor.
- J2: The junction between the 3.0 Ω and 16 Ω resistors.
- J3: The junction between the 4.0 Ω, 16 Ω, and 48 Ω resistors.
- J4: The node connected to the negative terminal of the battery. Note that the wire from J2 and the 48 Ω resistor both connect to this node.
The resistors R₁=3.0 Ω, R₂=4.0 Ω, and R₃=16 Ω form a delta (Δ) between nodes J1, J2, and J3. We can convert this delta into an equivalent wye (Y) network.
2. Perform the Delta-to-Wye (Δ-Y) Transformation
The formulas for the Y-network resistors (Ra, Rb, Rc) connected to a new central node (N) are:
- Sum of delta resistors: R_Δ = R₁ + R₂ + R₃ = 3.0 Ω + 4.0 Ω + 16 Ω = 23 Ω.
- Ra (connects J1 to N): Ra = (R₁ * R₂) / R_Δ = (3.0 * 4.0) / 23 = 12/23 Ω ≈ 0.522 Ω.
- Rb (connects J2 to N): Rb = (R₁ * R₃) / R_Δ = (3.0 * 16) / 23 = 48/23 Ω ≈ 2.09 Ω.
- Rc (connects J3 to N): Rc = (R₂ * R₃) / R_Δ = (4.0 * 16) / 23 = 64/23 Ω ≈ 2.78 Ω.
3. Analyze the Simplified Circuit
After replacing the delta with the wye, the circuit becomes much simpler:
- Resistor Ra is now in series with the rest of the circuit.
- From the new node N, we have two parallel branches connected to the negative terminal (J4):
- Branch 1: Resistor Rb is connected between N and J2. Since J2 is wired directly to J4, this branch just contains Rb.
- Branch 2: Resistor Rc is connected between N and J3. Resistor R₄=48 Ω connects J3 to J4. So, this branch has Rc and the 48 Ω resistor in series.
4. Calculate the Equivalent Resistance (R_eq)
- Resistance of Branch 2: R_branch2 = Rc + 48 Ω = (64/23) Ω + 48 Ω = 1168/23 Ω ≈ 50.8 Ω.
- Equivalent resistance of the two parallel branches (R_p):
R_p = (Rb * R_branch2) / (Rb + R_branch2) = [(48/23) * (1168/23)] / [(48/23) + (1168/23)] = 2.0045 Ω. - Total equivalent resistance of the circuit:
R_eq = Ra + R_p = (12/23) Ω + 2.0045 Ω ≈ 0.522 Ω + 2.0045 Ω ≈ 2.527 Ω.
5. Find Voltages at Original Nodes
To find the current and voltage for the 16 Ω resistor, we need the potentials at nodes J2 and J3.
- Total current from the battery: I_total = V / R_eq = 12 V / 2.527 Ω ≈ 4.75 A.
- The voltage at node N is the voltage across the parallel combination: V_N = I_total * R_p ≈ 4.75 A * 2.0045 Ω ≈ 9.52 V.
- Potential at J2: Node J2 is connected directly to the negative terminal (J4), so its potential is 0 V.
- Potential at J3: This is the voltage across the 48 Ω resistor. First, find the current in Branch 2: I_branch2 = V_N / R_branch2 ≈ 9.52 V / 50.8 Ω ≈ 0.1875 A.
Then, V_J3 = I_branch2 * 48 Ω = 0.1875 A * 48 Ω = 9.0 V.
6. Calculate Final Answers
- Potential Difference (Part H): The potential difference across the 16 Ω resistor is the difference between V_J3 and V_J2.
V_16 = |V_J3 – V_J2| = |9.0 V – 0 V| = 9.0 V. - Current (Part G): Now use Ohm’s law for the 16 Ω resistor.
I_16 = V_16 / R_16 = 9.0 V / 16 Ω = 0.5625 A.
Rounding to two significant figures gives 0.56 A.
