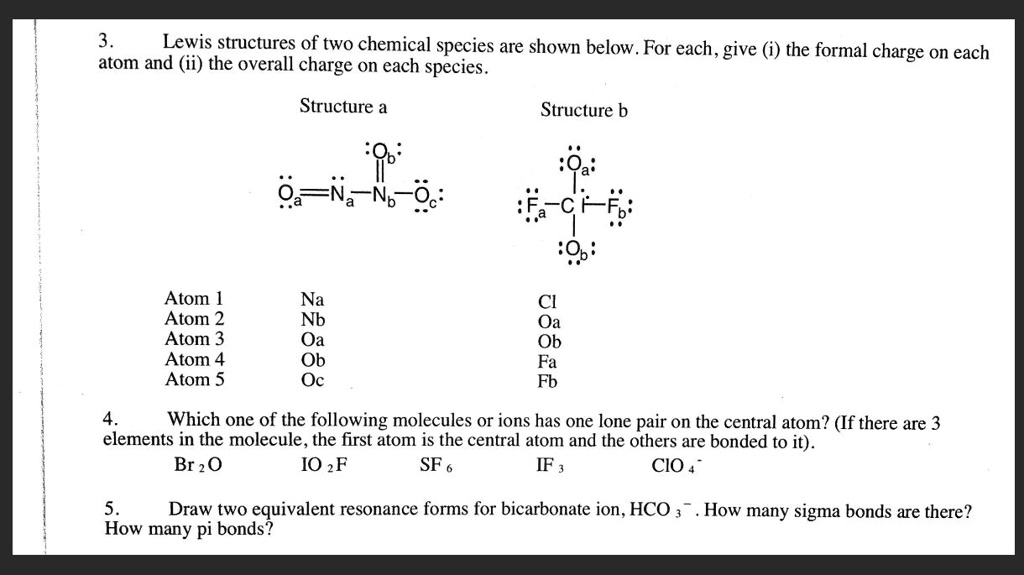
Lewis structures of two chemical species are shown below. For each, give the formal charge on each atom and (ii) the overall charge on each species. Structure a: Atom 1: C Atom 2: I Atom 3: O Atom 4: F Atom 5: S Structure b: Atom 1: O Atom 2: b Atom 3: O Atom 4: c Which one of the following molecules or ions has one lone pair on the central atom? (If there are 3 elements in the molecule, the first atom is the central atom and the others are bonded to it). Br2 IO2F SF IF3 CIO Draw two equivalent resonance forms for bicarbonate ion, HCO3-. How many sigma bonds are there? How many pi bonds?
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the correct answers to the chemistry questions.
3. Formal Charges and Overall Charge
The formal charge on an atom in a Lewis structure is calculated using the formula: Formal Charge = (Valence Electrons) – (Non-bonding Electrons) – (½ × Bonding Electrons). The overall charge of the species is the sum of the formal charges on all its atoms.
- Structure a (N₂O₃): The structure shown is Oₐ=Nₐ−N♭(=O♭)−O꜀.
- Nₐ: Has 5 valence electrons. It has 1 lone pair (2 non-bonding electrons) and 3 bonds (6 bonding electrons). Formal Charge = 5 − 2 − (½ × 6) = 0.
- N♭: Has 5 valence electrons. It has no lone pairs (0 non-bonding electrons) and 4 bonds (8 bonding electrons). Formal Charge = 5 − 0 − (½ × 8) = +1.
- Oₐ: Has 6 valence electrons. It has 2 lone pairs (4 non-bonding electrons) and a double bond (4 bonding electrons). Formal Charge = 6 − 4 − (½ × 4) = 0.
- O♭: Has 6 valence electrons. It has 2 lone pairs (4 non-bonding electrons) and a double bond (4 bonding electrons). Formal Charge = 6 − 4 − (½ × 4) = 0.
- O꜀: Has 6 valence electrons. It has 3 lone pairs (6 non-bonding electrons) and a single bond (2 bonding electrons). Formal Charge = 6 − 6 − (½ × 2) = -1.
- (ii) Overall Charge on Structure a: The sum of the formal charges is 0 + (+1) + 0 + 0 + (-1) = 0.
- Structure b ([ClO₂F₂]⁺): Assuming the central atom is Cl as listed, not C as drawn.
- Cl: Has 7 valence electrons. It has no lone pairs (0 non-bonding electrons) and 4 single bonds (8 bonding electrons). Formal Charge = 7 − 0 − (½ × 8) = +3.
- Oₐ and O♭: Each has 6 valence electrons, 3 lone pairs (6 non-bonding electrons), and 1 single bond (2 bonding electrons). Formal Charge = 6 − 6 − (½ × 2) = -1.
- Fₐ and F♭: Each has 7 valence electrons, 3 lone pairs (6 non-bonding electrons), and 1 single bond (2 bonding electrons). Formal Charge = 7 − 6 − (½ × 2) = 0.
- (ii) Overall Charge on Structure b: The sum of the formal charges is (+3) + (-1) + (-1) + 0 + 0 = +1.
4. Molecule or Ion with One Lone Pair on the Central Atom
The molecule with one lone pair on the central atom is IO₂F.
To determine this, we find the number of lone pairs on the central atom for each species. The central atom for IO₂F is Iodine (I).
- Total valence electrons in IO₂F = 7 (from I) + 2×6 (from O) + 7 (from F) = 26 electrons.
- Iodine is bonded to three other atoms (two O, one F). A stable Lewis structure that minimizes formal charges will have two double bonds to oxygen and one single bond to fluorine (O=I(=O)−F).
- In this structure, Iodine forms 5 bonds (using 10 electrons) and has a complete valence shell of 12 electrons (an expanded octet, which is common for elements in period 3 and below).
- The number of electrons on the central iodine atom is 12. Ten are bonding electrons. The remaining 12 − 10 = 2 electrons form one lone pair.
- The other options do not have one lone pair on the central atom: Br₂O has two lone pairs on the central oxygen; SF₆ and ClO₄⁻ have zero lone pairs; and IF₃ has two lone pairs.
5. Resonance Forms and Bonding in Bicarbonate Ion (HCO₃⁻)
The bicarbonate ion has two equivalent resonance forms. In both structures, the carbon atom is central. It is single-bonded to an OH group and has one single bond and one double bond to the other two oxygen atoms. The negative charge is delocalized between these two oxygen atoms.
- Resonance Form 1: Carbon is double-bonded to the “top” oxygen and single-bonded to the “right” oxygen, which holds the negative charge.
- Resonance Form 2: Carbon is single-bonded to the “top” oxygen (which now holds the negative charge) and double-bonded to the “right” oxygen.
- Sigma (σ) and Pi (π) Bonds: We can count the bonds in either resonance structure.
- There is one sigma bond between H and O.
- There is one sigma bond between O and C.
- There is one sigma bond in the C-O single bond.
- There is one sigma bond within the C=O double bond.
- This gives a total of 4 sigma bonds.
- There is one pi bond within the C=O double bond.
- This gives a total of 1 pi bond.
