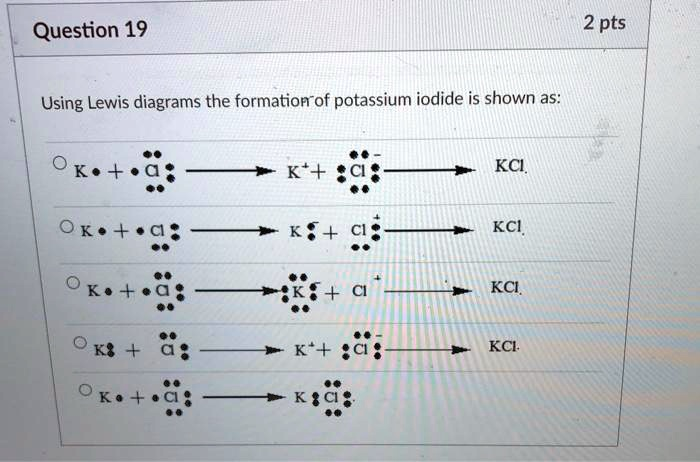
Using Lewis diagrams, the formation of potassium iodide is shown as: K
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The correct option is the first one.
Explanation:
The question asks for the Lewis diagram that correctly shows the formation of an ionic compound, although it mistakenly says “potassium iodide” while the options show the formation of “potassium chloride” (KCl). The process for both is analogous, involving a Group 1 metal and a Group 17 halogen.
- Identify the Reactants and Their Valence Electrons:
- Potassium (K) is an alkali metal in Group 1 of the periodic table. It has one valence electron. Its Lewis dot symbol is K•.
- Chlorine (Cl) is a halogen in Group 17. It has seven valence electrons. Its Lewis dot symbol shows the “Cl” symbol surrounded by seven dots.
- Determine the Bonding Type:
The bond forms between a metal (potassium) and a nonmetal (chlorine). This large difference in electronegativity leads to the formation of an ionic bond. In ionic bonding, electrons are transferred from the metal atom to the nonmetal atom, rather than shared. - Illustrate the Electron Transfer:
- To achieve a stable electron configuration (like a noble gas), the potassium atom will lose its single valence electron. By losing one electron, it becomes a positively charged ion, or cation (K⁺).
- The chlorine atom needs one more electron to complete its outer shell and achieve a stable octet (eight valence electrons). It will accept the electron lost by potassium, becoming a negatively charged ion, or anion (Cl⁻).
- Analyze the Correct Lewis Diagram:
The first option correctly depicts this entire process:- Reactants: It starts with the correct Lewis symbols for the neutral atoms: K• and a Cl atom with seven valence dots.
- Electron Transfer and Ion Formation: It shows the result of the electron transfer. Potassium becomes K⁺ (having lost its valence electron, no dots are shown), and chlorine becomes the chloride ion, shown with a complete octet of eight dots and a negative charge [ :Ċl: ]⁻.
- Final Product: The electrostatic attraction between the positive K⁺ ion and the negative Cl⁻ ion forms the ionic compound KCl.
The other options are incorrect because they either show the wrong initial number of valence electrons, depict electrons transferring in the wrong direction, or incorrectly represent the resulting ions or bond type.
