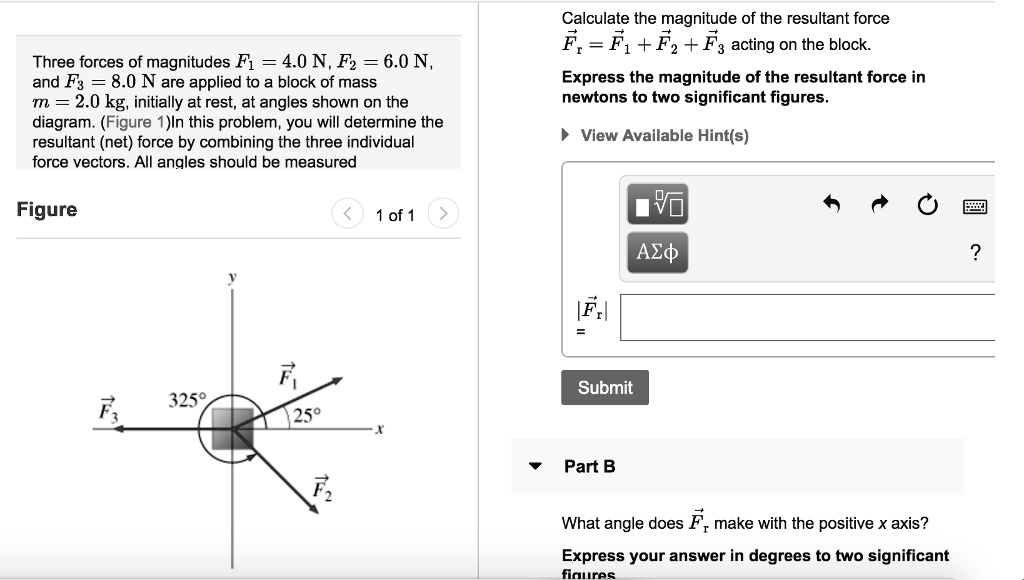
Three forces of magnitudes , , and are applied to a block of mass , initially at rest, at angles shown on the diagram.
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Correct Answer: 1.8
Explanation
To find the magnitude of the resultant force, we must first determine the x and y components of each individual force vector and then sum them to find the components of the resultant force. The magnitude can then be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. All angles are measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis.
1. Decompose each force into its x and y components:
- Force F₁:
The magnitude is |F₁| = 4.0 N, and the angle is θ₁ = 25°.
F₁x = |F₁| cos(θ₁) = 4.0 N * cos(25°) ≈ 3.63 N
F₁y = |F₁| sin(θ₁) = 4.0 N * sin(25°) ≈ 1.69 N - Force F₂:
The magnitude is |F₂| = 6.0 N, and the angle is θ₂ = 325°. This angle is in the fourth quadrant.
F₂x = |F₂| cos(θ₂) = 6.0 N * cos(325°) ≈ 4.91 N
F₂y = |F₂| sin(θ₂) = 6.0 N * sin(325°) ≈ -3.44 N - Force F₃:
The magnitude is |F₃| = 8.0 N, and it points directly along the negative x axis, so its angle is θ₃ = 180°.
F₃x = |F₃| cos(θ₃) = 8.0 N * cos(180°) = -8.0 N
F₃y = |F₃| sin(θ₃) = 8.0 N * sin(180°) = 0 N
2. Sum the components to find the resultant force components (F_rx and F_ry):
- Sum of x components:
F_rx = F₁x + F₂x + F₃x = 3.63 N + 4.91 N + (-8.0 N) = 0.54 N - Sum of y components:
F_ry = F₁y + F₂y + F₃y = 1.69 N + (-3.44 N) + 0 N = -1.75 N
3. Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force |F_r|:
Using the Pythagorean theorem, |F_r| = √(F_rx² + F_ry²).
|F_r| = √((0.54 N)² + (-1.75 N)²)
|F_r| = √(0.2916 N² + 3.0625 N²)
|F_r| = √(3.3541 N²)
|F_r| ≈ 1.831 N
The problem requires the answer to be expressed in newtons to two significant figures. Rounding 1.831 N gives 1.8 N.
