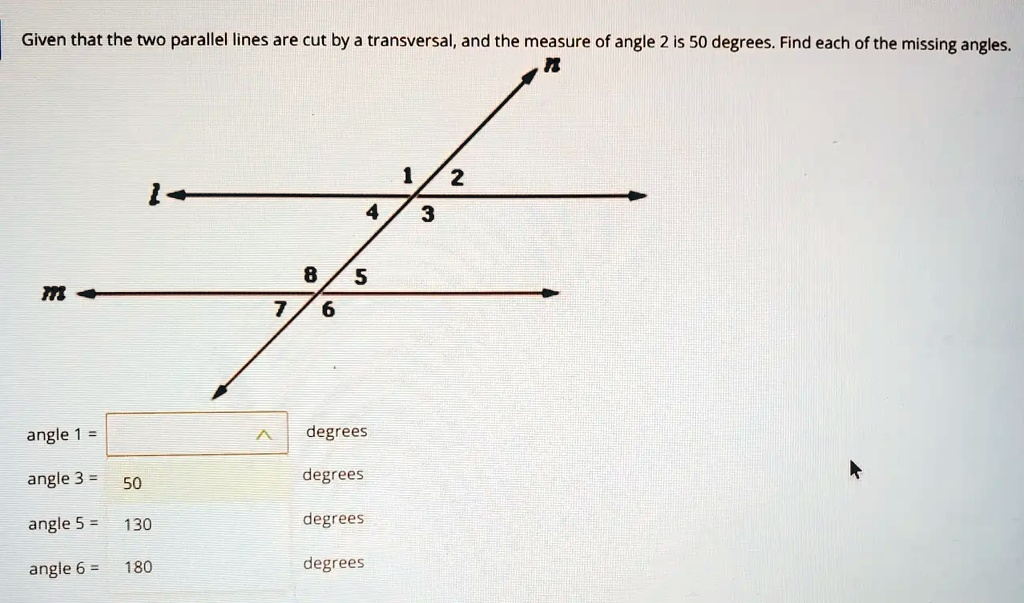
Given that the two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, and the measure of angle 2 is 50 degrees. Find each of the missing angles. angle 1 = degrees angle 3 = 50 degrees angle 5 = 130 degrees angle 6 = 180 degrees
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Based on the provided image and the principles of geometry, here are the correct measures for the missing angles.
angle 1 = 130 degrees
angle 3 = 130 degrees
angle 5 = 130 degrees
angle 6 = 50 degrees
Explanation
This geometry problem involves two parallel lines, l and m, intersected by a third line called a transversal, n. We are given that the measure of angle 2 is 50 degrees. We can find the measures of all other angles by applying a few key geometric rules.
To find the measure of angle 1:
Angle 1 and angle 2 are a linear pair, which means they are adjacent angles that form a straight line. The sum of the angles in a linear pair is always 180 degrees. Therefore, to find the measure of angle 1, we subtract the measure of angle 2 from 180.
Measure of angle 1 = 180° – 50° = 130°.
To find the measure of angle 3:
Angle 3 and angle 1 are vertical angles. Vertical angles are opposite each other at an intersection and are always equal in measure. Since we found that angle 1 is 130 degrees, angle 3 must also be 130 degrees. Alternatively, angle 3 and angle 2 form a linear pair, so its measure is 180° – 50° = 130°. The value of 50 degrees shown in the image for angle 3 is incorrect.
To find the measure of angle 6:
Angle 6 and angle 2 are corresponding angles. Corresponding angles are in the same relative position at each intersection. When the lines intersected by the transversal are parallel, their corresponding angles are equal. Thus, the measure of angle 6 is the same as the measure of angle 2.
Measure of angle 6 = 50°. The value of 180 degrees shown in the image for angle 6 is incorrect.
To find the measure of angle 5:
Angle 5 and angle 3 are alternate interior angles. These are angles on opposite sides of the transversal and between the two parallel lines. For parallel lines, alternate interior angles are equal. Since we determined angle 3 is 130 degrees, angle 5 must also be 130 degrees. We can also see that angle 5 and angle 6 form a linear pair, so their sum is 180 degrees. Using the value we found for angle 6 (50°), we get 180° – 50° = 130°
