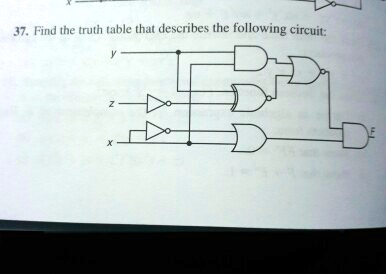
Find the truth table that describes the following circuit:
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Of course. Here is the correct truth table and a detailed explanation of how it is derived from the provided logic circuit diagram.
Correct Answer: The Truth Table
| x | y | z | F |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Explanation
To determine the final output, F, we must analyze the circuit step by step, evaluating the output of each logic gate based on its inputs. The circuit has three primary inputs, x, y, and z, which means the truth table will have 2^3 = 8 possible input combinations.
First, let’s identify the individual gates and their connections. The circuit contains two NOT gates (inverters), one AND gate, one XOR gate, one OR gate, one NOR gate (an OR gate with an inverted output), and a final AND gate that produces the output F.
- Initial Inversions: The inputs x and z are immediately inverted by NOT gates. We will refer to their outputs as x’ and z’.
- First Level of Gates:
- A top AND gate takes y and z’ as its inputs. Its output is (y AND z’).
- A middle XOR gate also takes y and z’ as its inputs. Its output is (y XOR z’).
- A bottom OR gate takes x’ and y as its inputs. Its output is (x’ OR y).
- Second Level Gate (NOR Gate): The outputs of the top AND gate and the middle XOR gate feed into a NOR gate. A NOR gate first performs an OR operation on its inputs and then inverts the result. So, the output of this gate is ((y AND z’) OR (y XOR z’))’.
- Final Gate (AND Gate): The final output, F, is produced by an AND gate. Its two inputs are:
- The output from the NOR gate: ((y AND z’) OR (y XOR z’))’.
- The output from the bottom OR gate: (x’ OR y).
Therefore, the complete Boolean expression for the circuit is:
F = [ ((y AND z’) OR (y XOR z’))’ ] AND (x’ OR y)
By evaluating this expression for each of the eight possible input combinations of x, y, and z, we can fill out the truth table. For example, for the input (x=0, y=0, z=1), we get x’=1 and z’=0. The expression becomes [ ((0 AND 0) OR (0 XOR 0))’ ] AND (1 OR 0). This simplifies to [ (0 OR 0)’ ] AND (1), which is (0)’ AND 1, or 1 AND 1, resulting in F=1. For all other input combinations, the final result is 0.
