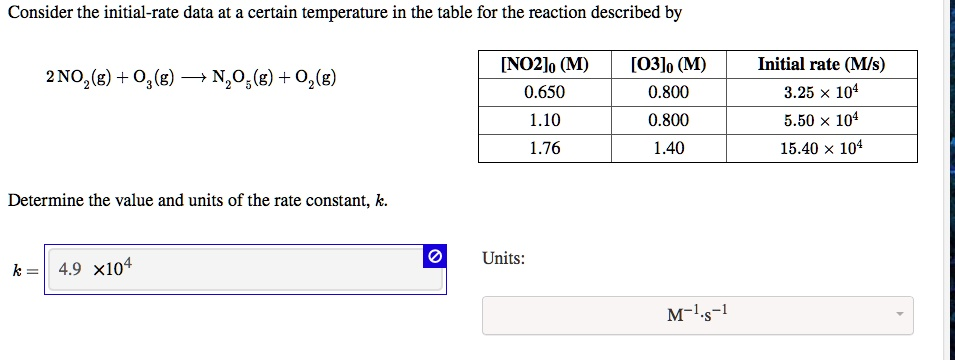
Consider the initial-rate data at a certain temperature in the table for the reaction described by: [NO2]o (M) 0.650 1.10 1.76 O3 0.800 0.800 1.40 Initial rate (Ms) 3.25 x 10^4 5.50 x 10^4 15.40 x 10^4 2 NO2(g) + O3(g) -> N2O5(g) + O2(g) Determine the value and units of the rate constant, k. Units: 4.9 x 10^4 M^-1 s^-1
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
₃ (m) by comparing Experiments 2 and 3. We use the fact that n = 1:
(Rate₃ / Rate₂) = (k[NO₂]₃¹[O₃]₃ᵐ) / (k[NO₂]₂¹[O₃]₂ᵐ)
(15.40 x 10⁴) / (5.50 x 10⁴) = (k(1.76)¹(1.40)ᵐ) / (k(1.10)¹(0.800)ᵐ)
2.80 = (1.60) * (1.75)ᵐ
2.80 / 1.60 = (1.75)ᵐ
1.75 = (1.75)ᵐ
Therefore, m = 1. The reaction is first order in O₃.
The complete rate law is Rate = k[NO₂][O₃]. The overall reaction order is 1 + 1 = 2.
Now, we can calculate the rate constant, k, by rearranging the rate law and using data from any experiment. Using data from Experiment 1:
k = Rate / ([NO₂][O₃])
k = (3.25 x 10⁴ M/s) / (0.650 M * 0.800 M)
k = (3.25 x 10⁴ M/s) / (0.520 M²)
k = 62,500 M⁻¹·s⁻¹ = 6.25 x 10⁴ M⁻¹·s⁻¹
The units for k are derived from the rate law: Units of k = (M/s) / (M * M) = M⁻¹·s⁻¹.
