Describe the three layers of meninges by matching each layer with the description(s) that fit it best: The deepest layer “Spider-like” Tough; white; fibrous connective tissue Deep to the dura mater Very thin Follows the contours of the spinal cord The outer layer Consists of spider-web-like connective tissue Attached to the pia mater Two separate layered membranes Follows the contours of the dura Located next to the skull and vertebrae Dura Mater Arachnoid Mater Pia Mater
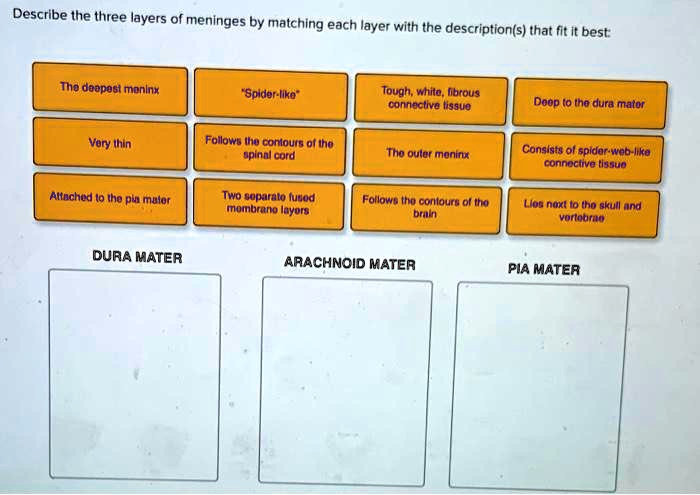
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
The meninges are three layers of connective tissue membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. Here is the correct matching of each layer with the descriptions based on the provided image:
- Dura Mater:
- Tough, white, fibrous connective tissue
- Two separate fused membrane layers
- Located next to the skull and vertebrae
- Deep to the dura mater
- Arachnoid Mater:
- Spider-like
- Consists of spider-web-like connective tissue
- Follows the contours of the brain
- Follows the contours of the spinal cord
- Pia Mater:
- Very thin
- Attached to the pia mater
- The outer layer
These layers play vital roles in protecting and supporting the central nervous system, providing both physical protection and nutrient delivery.
