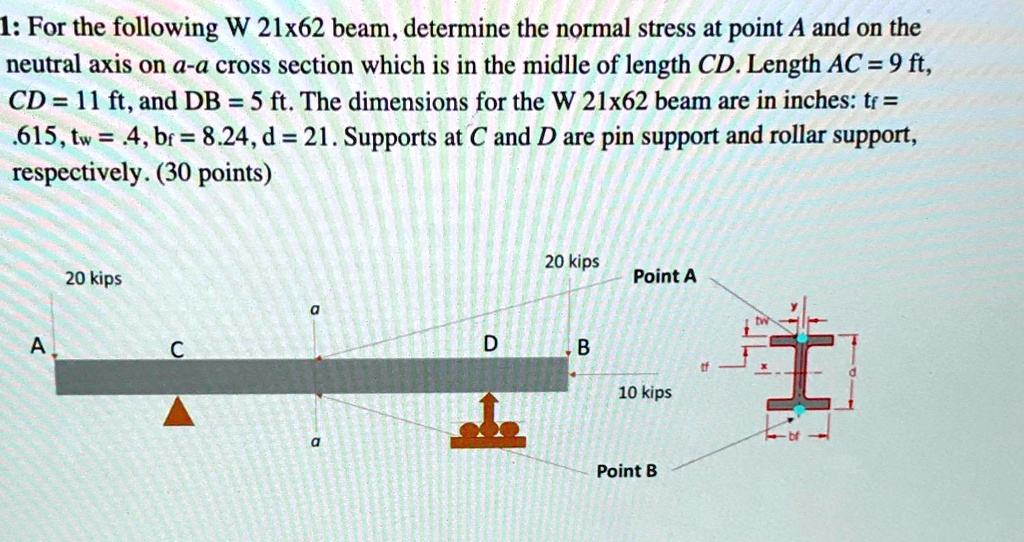
For the following W 21×62 beam, determine the normal stress at point A and on the neutural axis on a-a cross section which is in the midlle of length CD. Length AC = 9 ft, CD = 11 ft, and DB = 5 ft. The dimensions for the W 21×62 beam are in inches: tf = .615, tw = .4, bf = 8.24, d = 21. Supports at C and D are pin support and rollar support, respectively. (30 points)
The Correct Answer and Explanation is:
Here are the calculated normal stresses for the specified points on the W 21×62 beam.
Final Answer:
- The normal stress at Point A (top fiber) is -30.2 ksi (Compression).
- The normal stress on the neutral axis is 0.554 ksi (Tension).
Explanation:
The total normal stress (σ) at any point on the cross-section is the superposition of the stress due to the axial force (P) and the stress due to the bending moment (M). The governing equation is:
σ = P/A – My/I
Here is the step-by-step determination of the stresses:
1. Calculate Support Reactions
First, we find the reactions at the pin support C and roller support D using static equilibrium equations on the free-body diagram of the entire beam.
- Sum of moments about C = 0:
- (20 kips * 9 ft) + D_y * (11 ft) – (20 kips * 16 ft) = 0
- 11 * D_y = 180 kip-ft + 320 kip-ft = 500 kip-ft
- D_y = 45.45 kips (upward)
- Sum of horizontal forces = 0:
- C_x + 10 kips = 0 => C_x = -10 kips (acting to the left)
- Sum of vertical forces = 0:
- C_y + D_y – 20 kips – 20 kips = 0
- C_y + 45.45 kips – 40 kips = 0 => C_y = -5.45 kips (acting downward)
2. Determine Internal Forces at Cross-Section a-a
The cross-section a-a is in the middle of CD, which is 5.5 ft from C (or 14.5 ft from the left end A). We make a cut at this section and analyze the left portion.
- Axial Force (P): The internal axial force P must balance the external horizontal reaction C_x.
- P + C_x = 0 => P – 10 kips = 0 => P = 10 kips (Tension)
- Bending Moment (M): Summing moments about the cut (at x = 14.5 ft):
- M – (20 kips * 14.5 ft) – (5.45 kips * 5.5 ft) = 0
- M = 290 kip-ft + 29.975 kip-ft = 319.975 kip-ft
- M ≈ 320 kip-ft (This positive moment causes compression at the top and tension at the bottom).
- Convert to kip-inches: M = 320 kip-ft * 12 in/ft = 3840 kip-in.
3. Calculate Cross-Sectional Properties
Using the given dimensions for the W 21×62 beam (d=21, b_f=8.24, t_f=0.615, t_w=0.4, all in inches):
- Area (A):
A = 2*(b_f * t_f) + (d – 2t_f)t_w = 2(8.240.615) + (21 – 2*0.615)*0.4 = 18.04 in² - Moment of Inertia (I):
I = I_web + 2*(I_flange_centroid + A_flange * d_y²)
I = [ (1/12)0.4(19.77)³ ] + 2*[ (1/12)8.24(0.615)³ + (8.240.615)(10.1925)² ]
I = 257.6 + 2*(0.16 + 526.5) = 1310.8 in⁴
4. Calculate Normal Stresses
- Stress at Point A (Top Fiber):
Point A is at the top of the beam, so y = d/2 = +10.5 in.
σ_A = P/A – My/I = (10 kips / 18.04 in²) – (3840 kip-in * 10.5 in / 1310.8 in⁴)
σ_A = 0.554 ksi – 30.76 ksi = -30.21 ksi (Compression) - Stress at the Neutral Axis:
At the neutral axis, the distance y = 0. Therefore, the bending stress term is zero.
σ_NA = P/A – M(0)/I = P/A = 10 kips / 18.04 in²
σ_NA = +0.554 ksi (Tension)
